What is AI traffic in GA4?
AI traffic in GA4 refers to user interactions initiated or influenced by AI-driven applications or systems.
These applications or systems could be chatbots, virtual assistants, automated testing tools, or any software that uses AI to interact with web pages, apps, or services.
For example, if a user accesses your website by clicking a link generated by Perplexity AI in a normal browsing session, this would be considered AI traffic.
Why is understanding and analysing AI traffic crucial?
- You can personalise users’ experiences by analysing the impact of AI on user preferences.
- You can improve user journeys by identifying issues and trends in AI interactions.
- Target ads more effectively with insights from AI-driven traffic data.
- Assess and enhance AI’s effectiveness in attracting engaged visitors.
- Anticipate trends to innovate and stay competitive in evolving markets.
By harnessing the power of AI traffic analysis, businesses can unlock a deeper understanding of their users, optimise their offerings, and make data-driven decisions for a thriving online presence.
Overview of AI traffic analysis reports in GA4.
To conduct AI traffic analysis in GA4, we will create a new exploration report from scratch. This new report would have nine tabs.
Each tab displays a sub-report that measures the performance of your AI traffic.
The following are the nine sub-reports we would create in our exploration report:
#1 Overview – This report provides an overview of each AI traffic source:
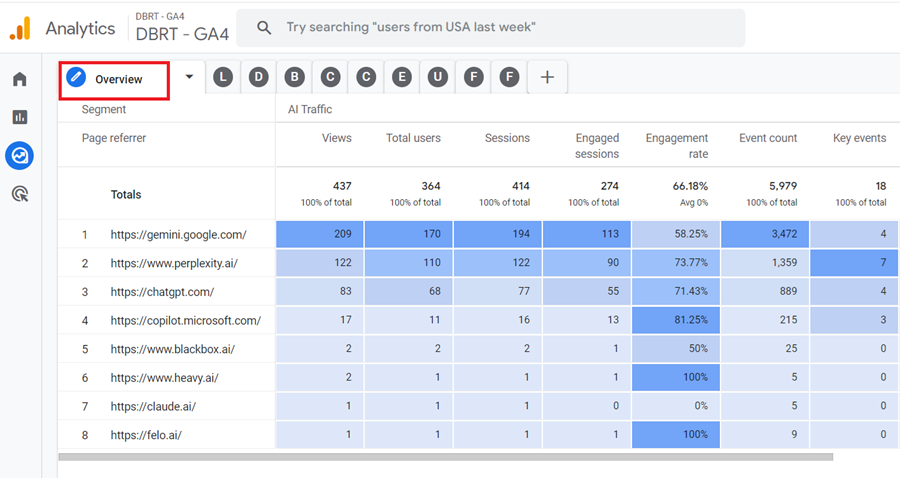
#2 Landing Pages – Use this report to measure the performance of landing pages from AI traffic:
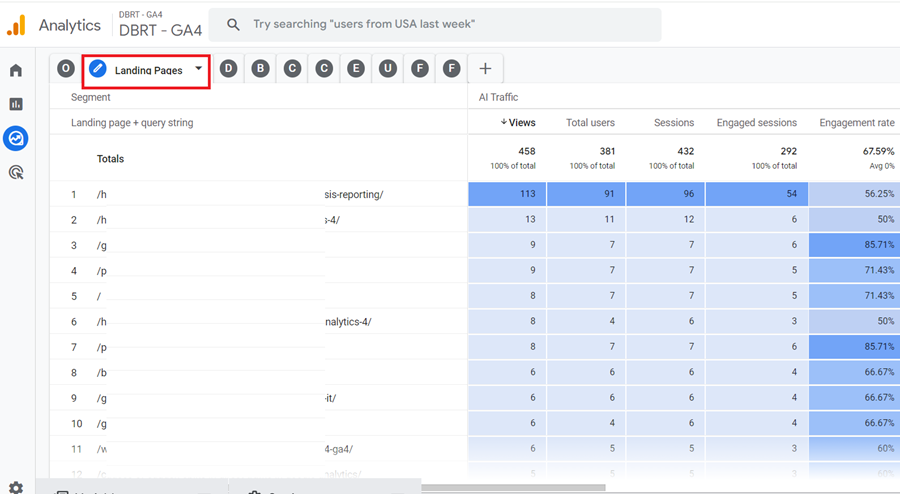
#3 Devices – Use this report to measure the performance of different devices (desktop, mobile, smart TV, tablet) which sent AI traffic to your website:
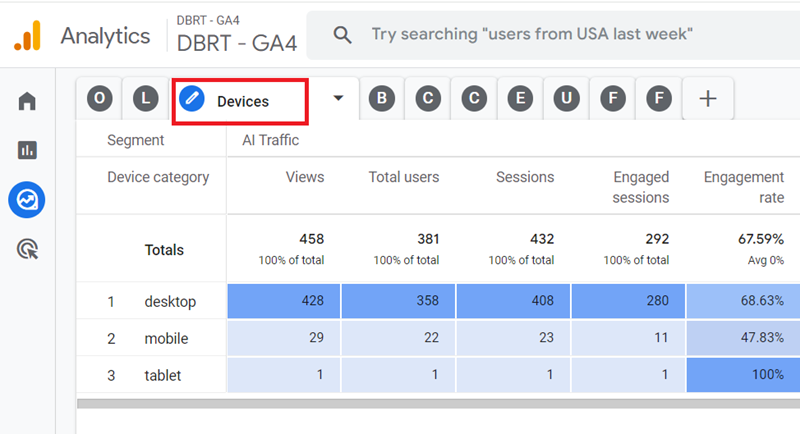
#4 Browsers – Use this report to measure the performance of different web browsers which sent AI traffic to your website:
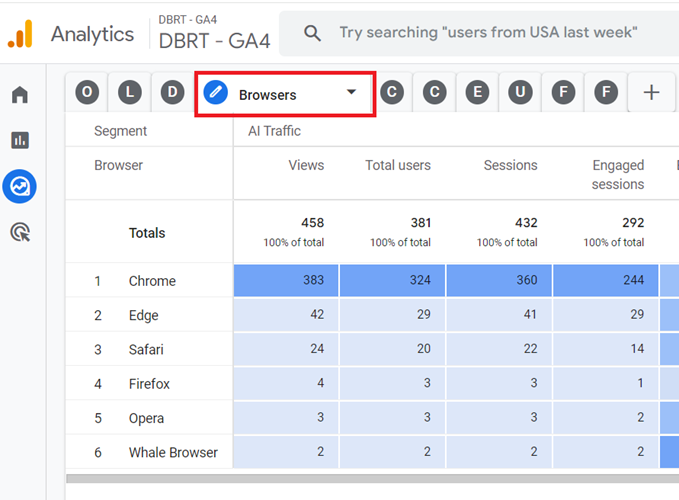
#5 Countries – Use this report to determine the countries which sent AI traffic to your website:
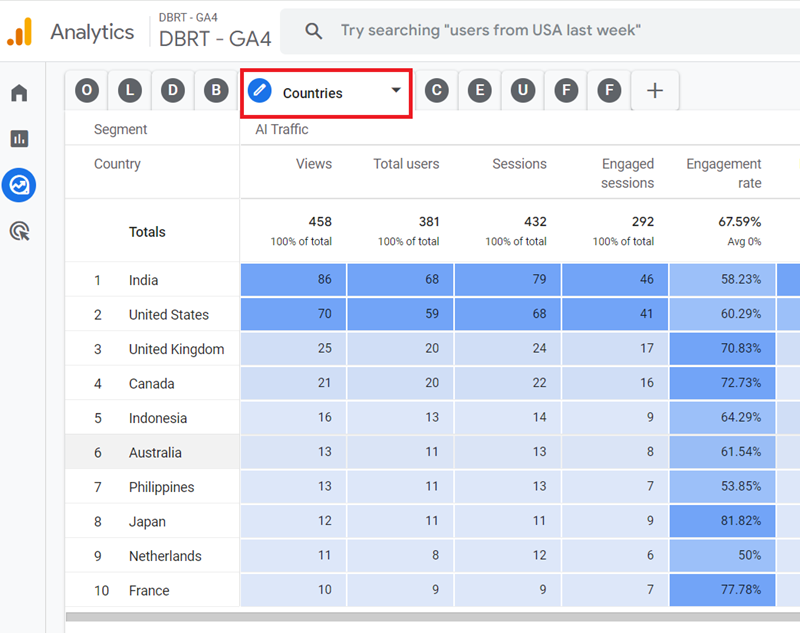
#6 Conversions – Use this report to determine all the conversions (key events) generated by AI traffic on your website:
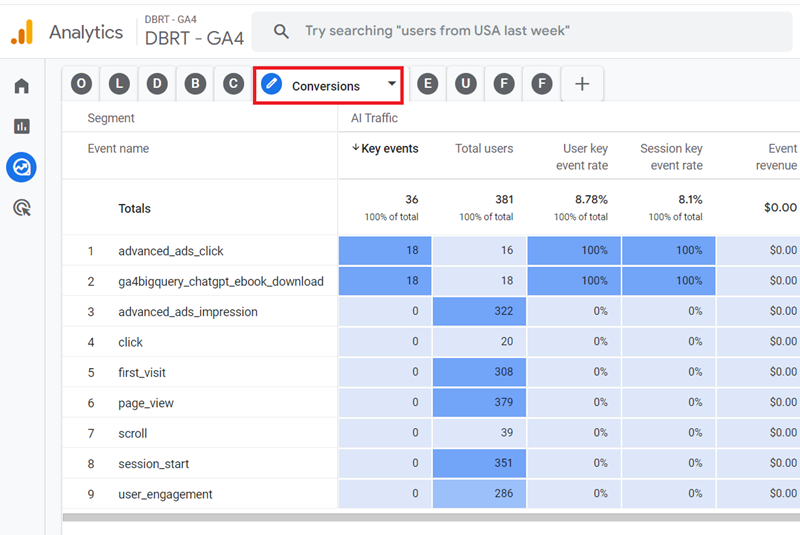
#7 ECommerce – Use this report to measure the ecommerce performance of AI traffic to your website:
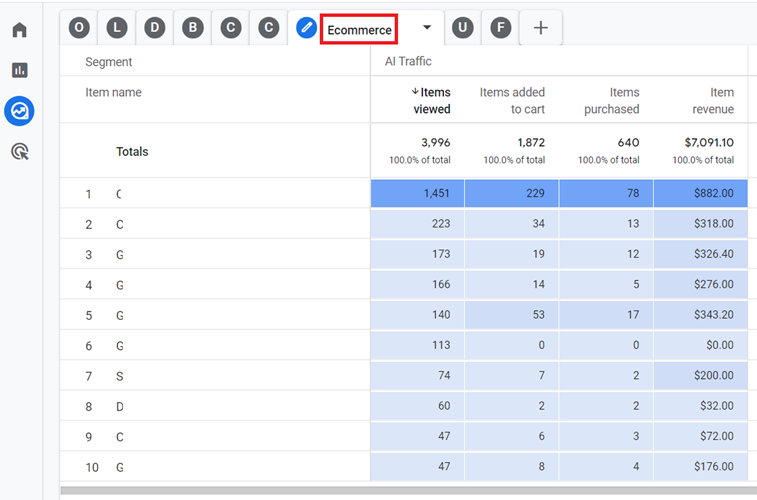
#8 User Flow – Use this report to determine how the AI traffic is using your website:
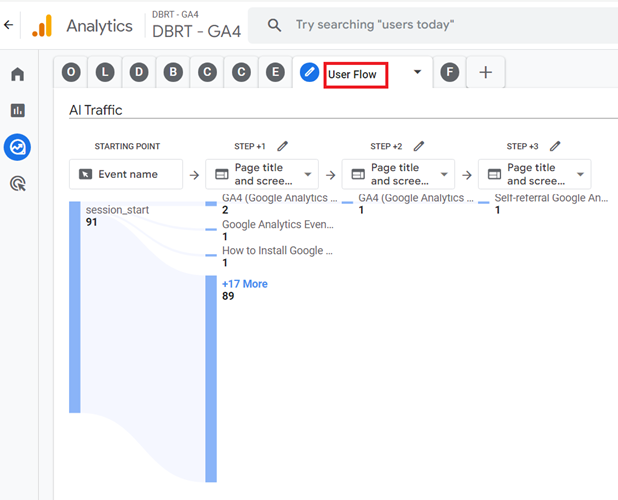
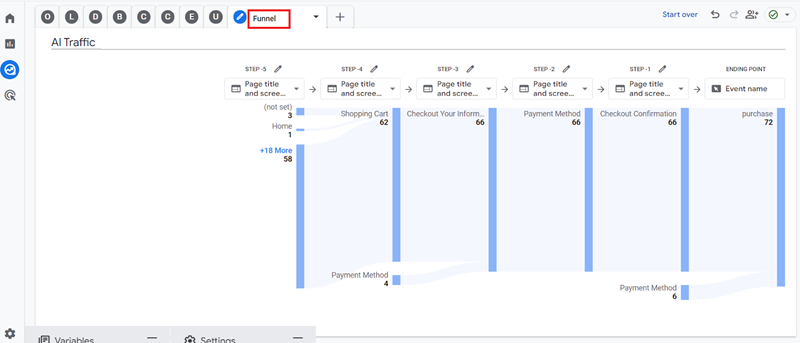
#9 Funnel – Use this report to determine how AI traffic is converting on your website:
How to create the AI traffic reports in GA4?
Follow the steps below to create the AI traffic tracking report in GA4:
Step-1: Login to your GA4 property.
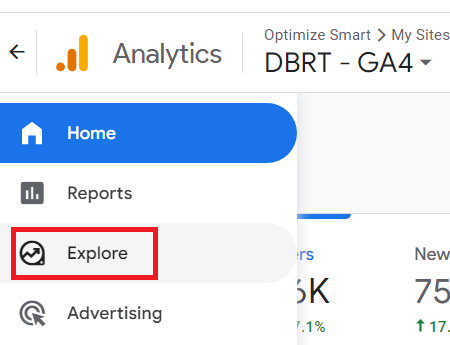
Step-2: Click on Explore from the left-hand side menu:
Step-3: Scroll down and navigate to the report named ‘Organic Search Traffic Analysis‘:
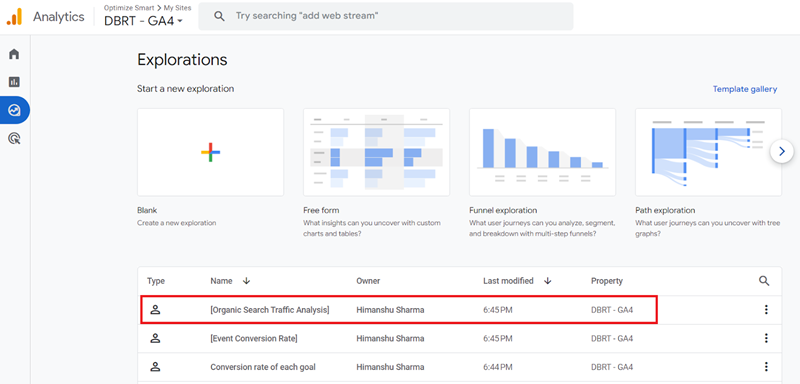
Note: If you do not already have this report, then stop reading this article for now and create this report first. We will use this report as a template to create a new report. Follow the instructions in this article: Organic Search Traffic Analysis in GA4 – Complete Guide.
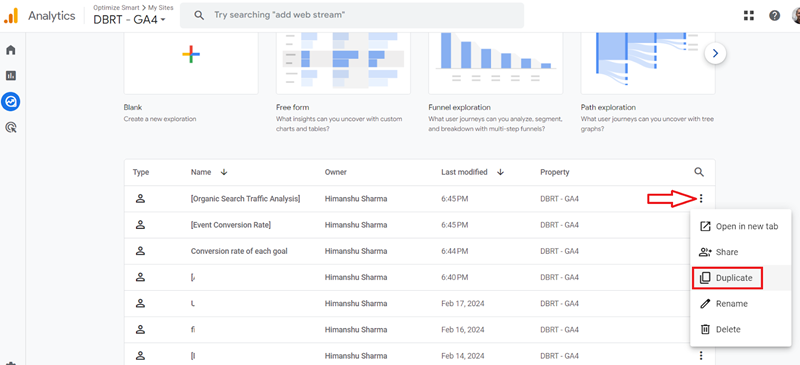
Step-4: Click on the three dots menu next to the ‘Organic Search Traffic Analysis’ report and then click on the ‘Duplicate‘ option from the drop-down menu:
Step-5: Click on ‘Copy of [Organic Search Traffic Analysis]‘ to open the report:
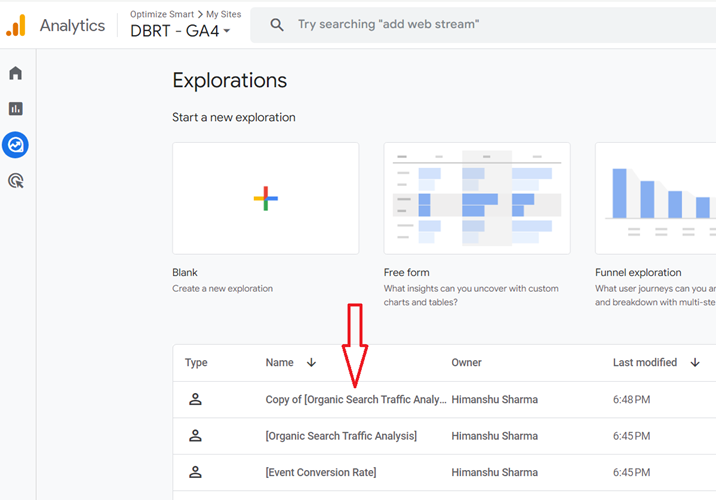
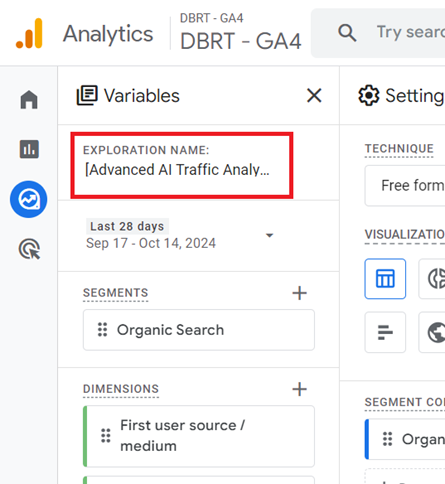
Step-6: Rename the report to [Advanced AI Traffic Analysis]:
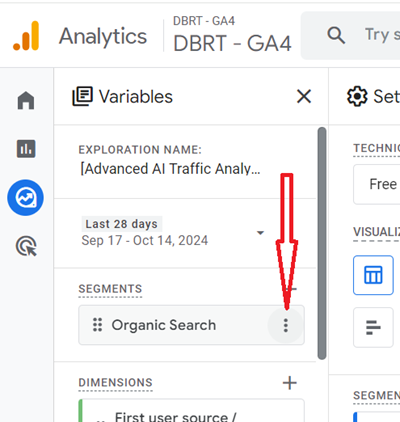
Step-7: Hover your mouse over the ‘Organic Search‘ segment and then click on the three dots menu next to it:
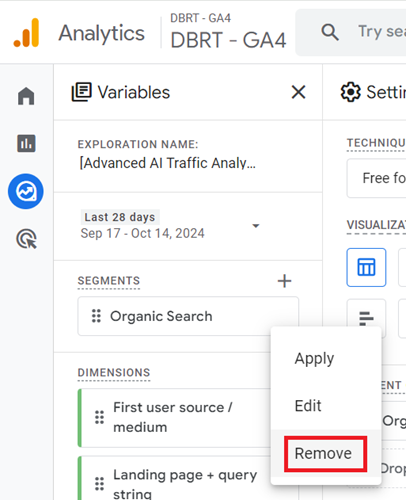
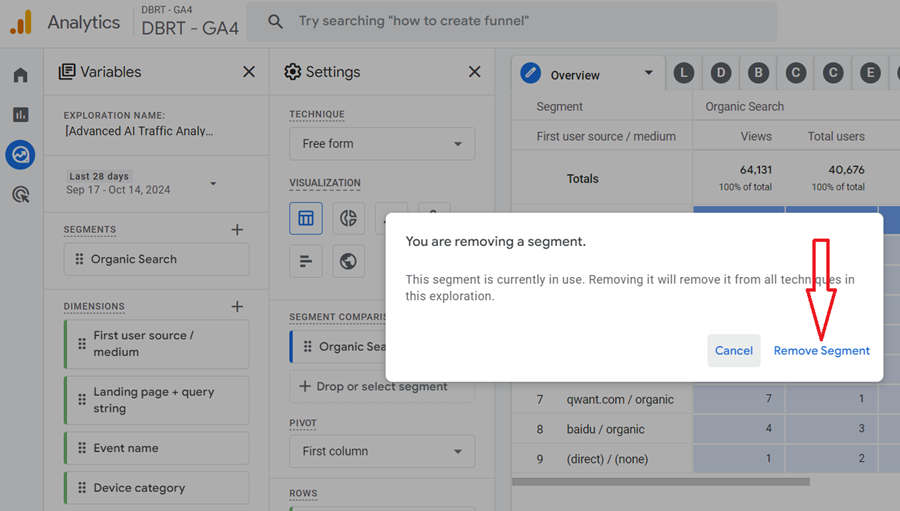
Step-8: Click on the ‘Remove‘ option from the drop-down menu:
Step-9: Click on the ‘Remove Segment‘ button:
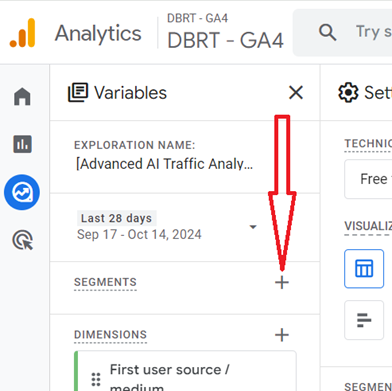
Step-10: Click on the + button next to SEGMENTS to add a new segment:
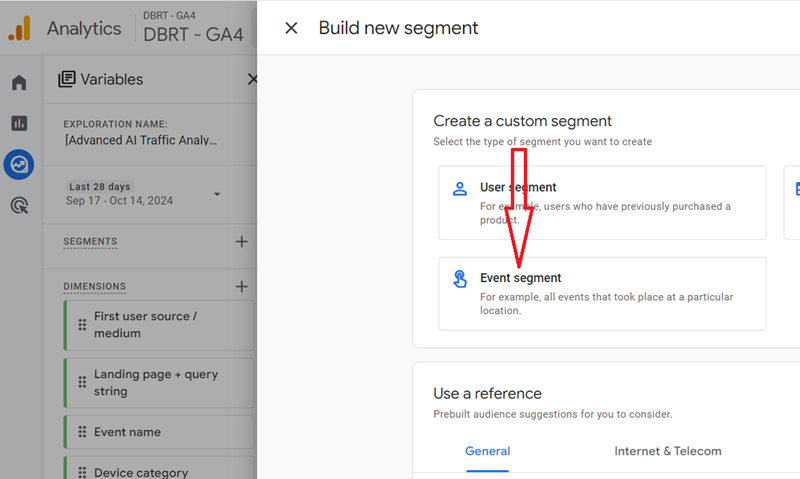
Step-11: Click on ‘Event Segment’:
Step-12: Define your segment like the one below and then click on the ‘Save and Apply’ button:
Segment Name: AI Traffic
Include events when:
Page referrer matches regex ^.*\.ai/.*|.*\.openai.*|.*copilot.*|.*chatgpt.*|.*gemini.*$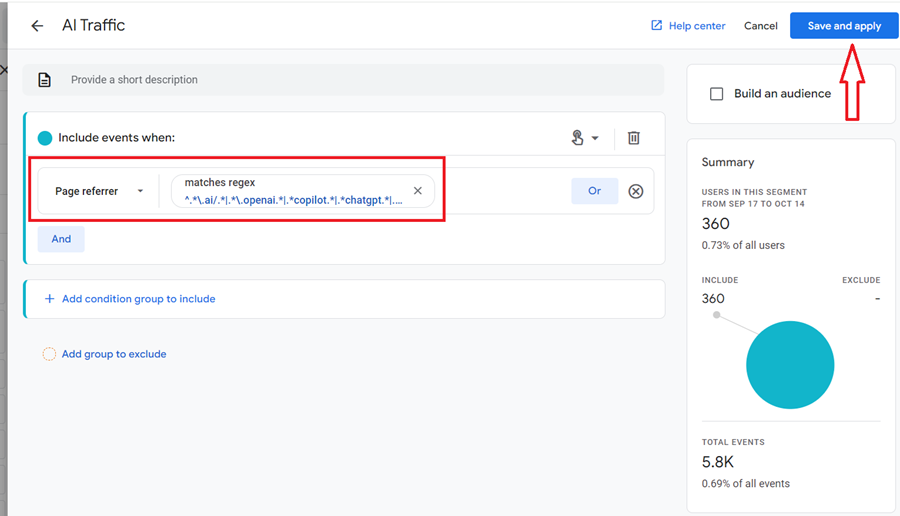
You should now see your new segment listed under the ‘SEGMENTS’ column:
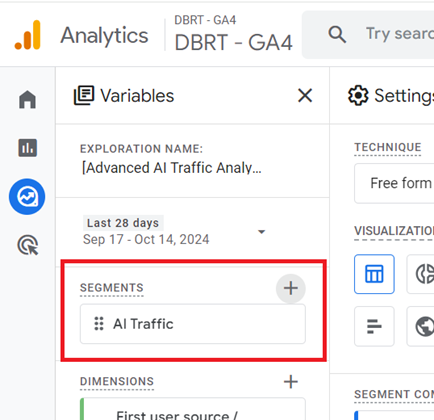
Step-13: Make sure that you are looking at the report under the ‘Overview’ tab:
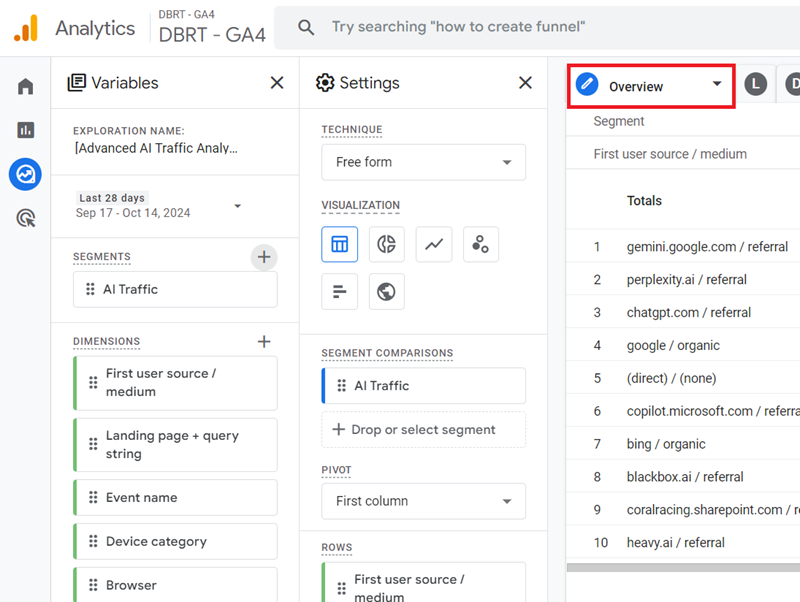
Step-14: Hover your mouse over the dimension ‘First user source / medium‘ and then click on the cross button next to it to delete it from the canvas on the right:
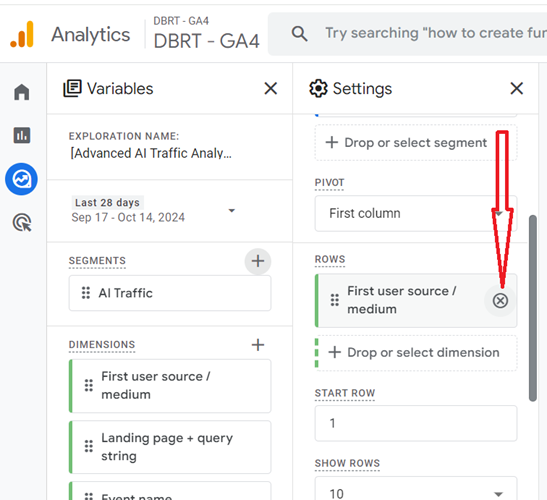
You should now see a screen like the one below:
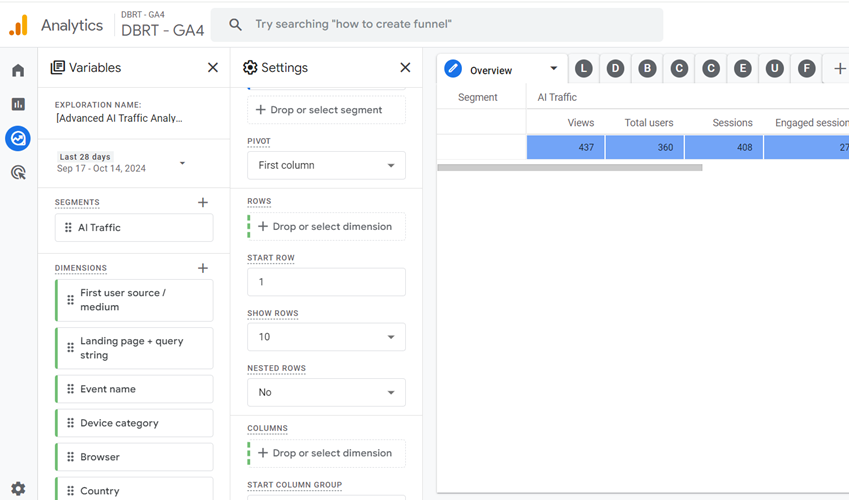
Step-15: Import the dimension ‘Page referrer’ to the report:
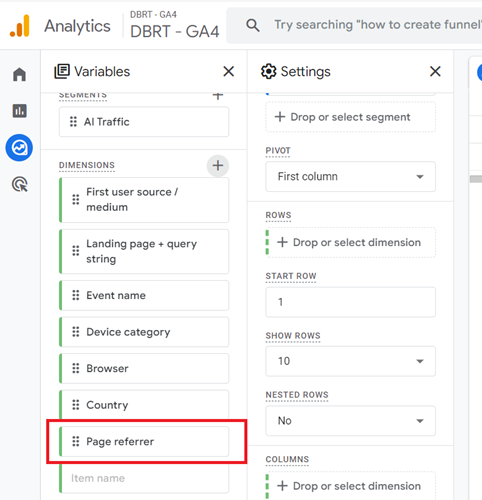
Step-16: Double-click on the dimension ‘Page referrer’ so that it is automatically added to the canvas on the right:
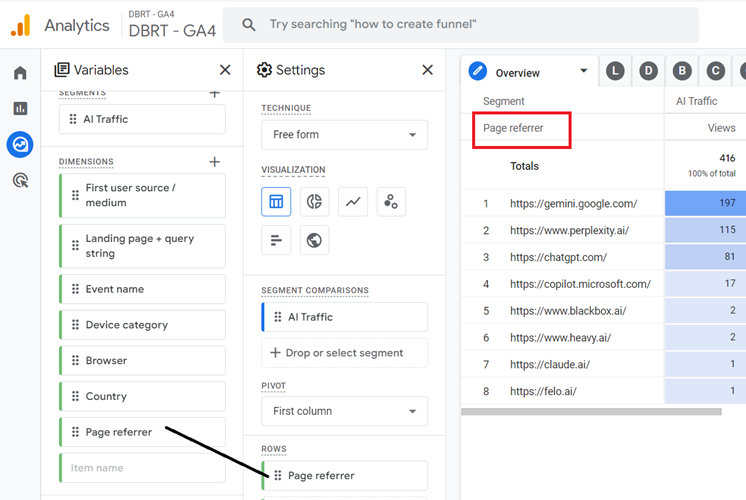
The AI traffic overview report would look like the one below:
Step-17: Click on the ‘Landing page’ tab:
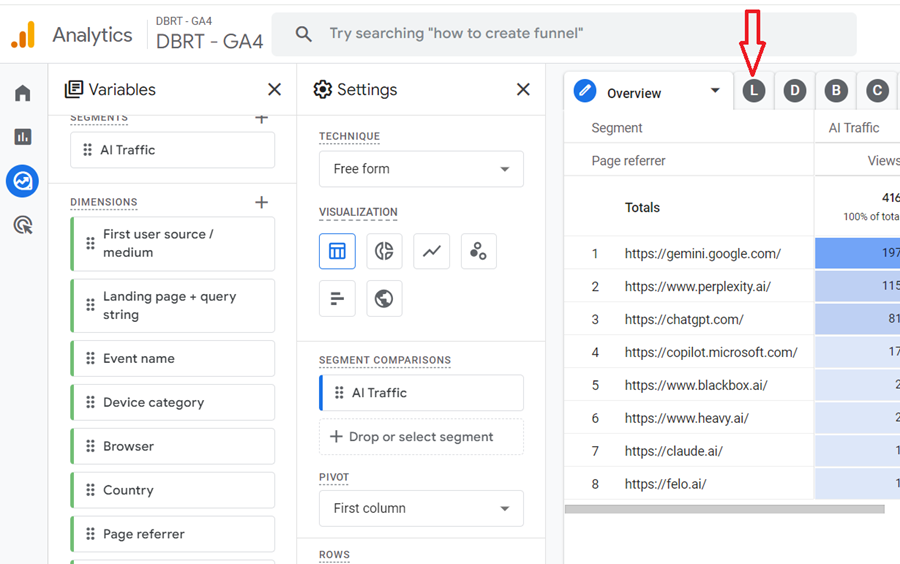
Step-18: Hover your mouse over the ‘AI Traffic’ segment to display the three dots menu:
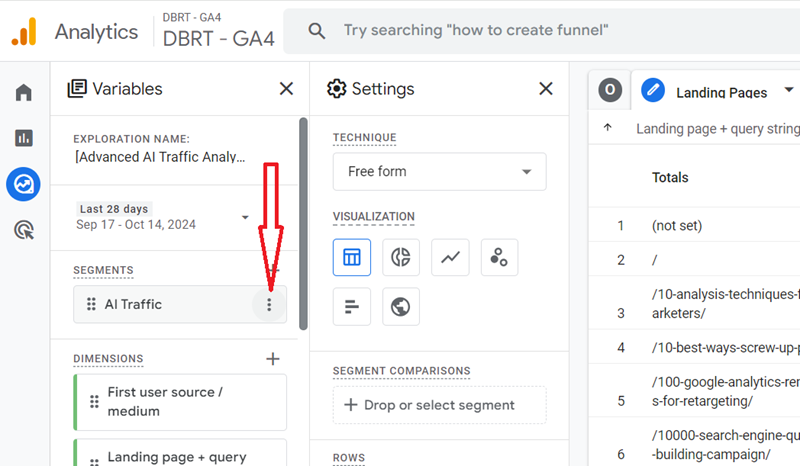
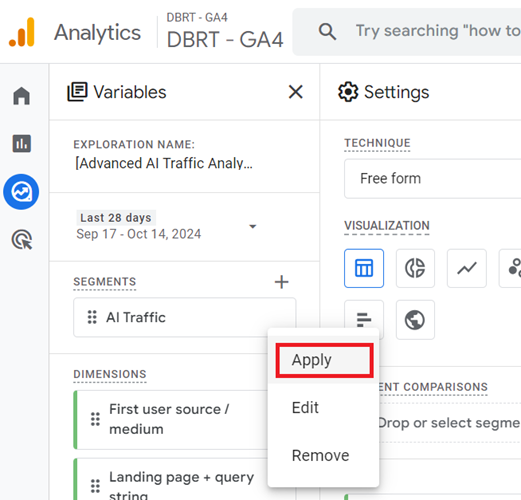
Step-19: Click on the ‘Apply’ button from the drop-down menu:
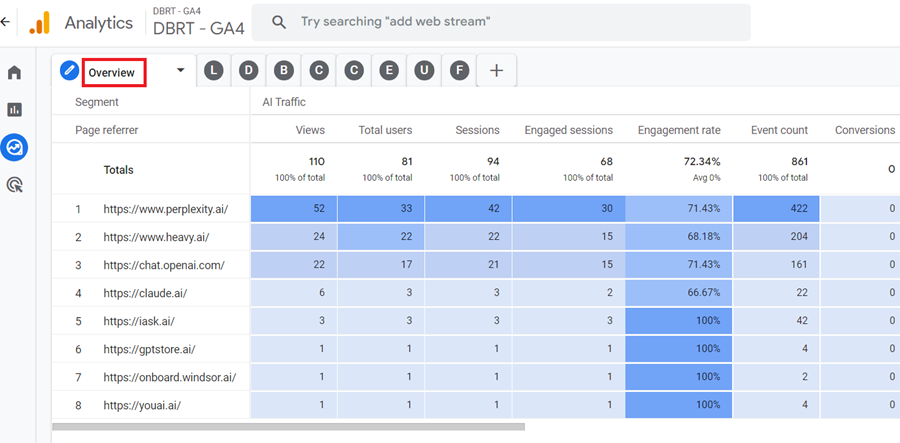
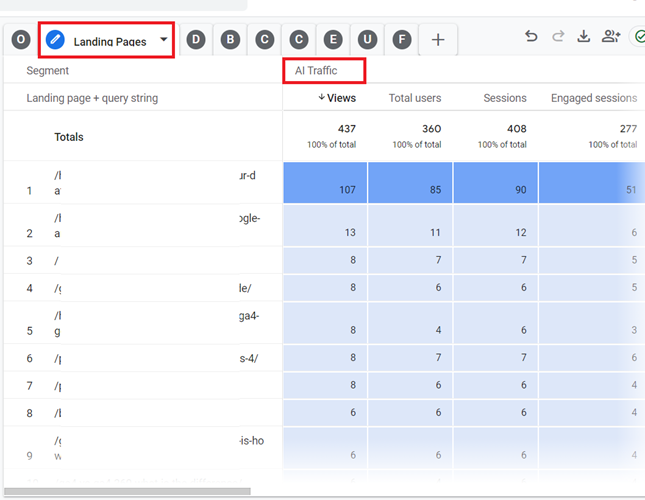
You should now see the ‘Landing Pages’ report for the AI traffic like the one below:
Step-20: Click on the remaining 7 tabs of your exploration report one by one and then apply the ‘AI traffic’ segment to them as described earlier.
That’s how you can create various reports to track AI traffic in GA4.
Introduction to AI Traffic Channel Group.
Since AI chatbots are becoming significant website traffic sources, grouping AI-referred traffic into a single channel has become very important.
AI traffic in GA4 is currently categorised under “referral” via dozens of different referrers. A custom channel group helps separate this unique traffic type for better data analysis.
An AI Traffic channel group in GA4 can be used as primary or secondary dimensions in reports and for creating audience conditions, allowing for a more detailed and flexible analysis of AI-referred traffic.
The channel group can also be applied retroactively.
When you create a new channel group for AI traffic in GA4, it will automatically be applied to all historical data in your GA4 property.
This means you can immediately analyse past AI-referred traffic without waiting for new data to accumulate.
Creating an AI Traffic Channel Group in GA4.
Follow the steps below to create a new AI Traffic Channel group in GA4:
Step-1: Navigate to GA4 Admin > Data Display > Channel groups.
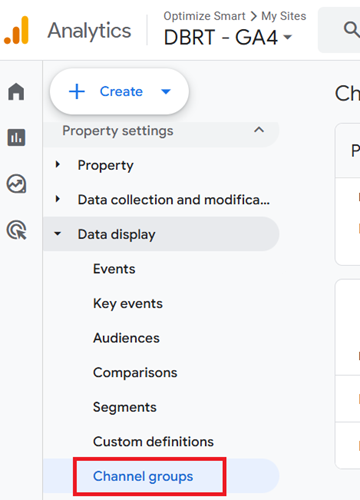
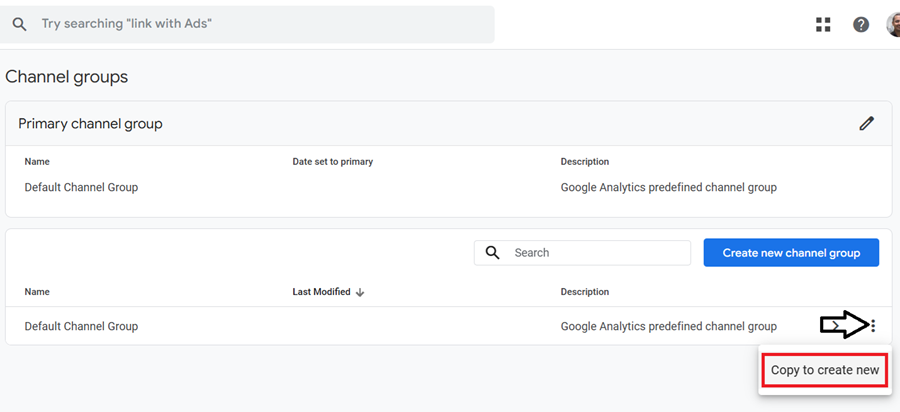
Step-2: Click on the three dots menu next to the default channel group and then click on ‘Copy to create new‘.
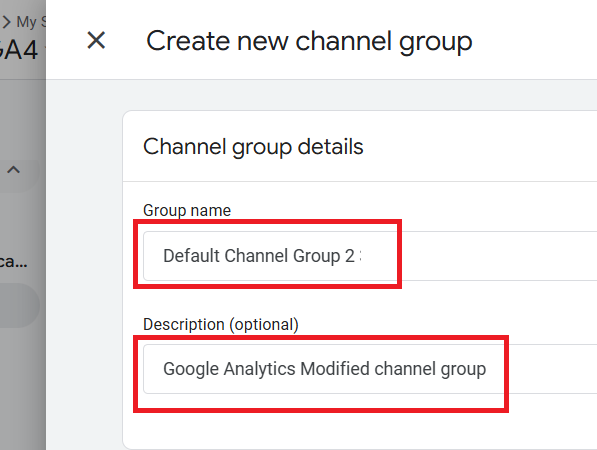
Step-3: Rename your new channel group and update the description:
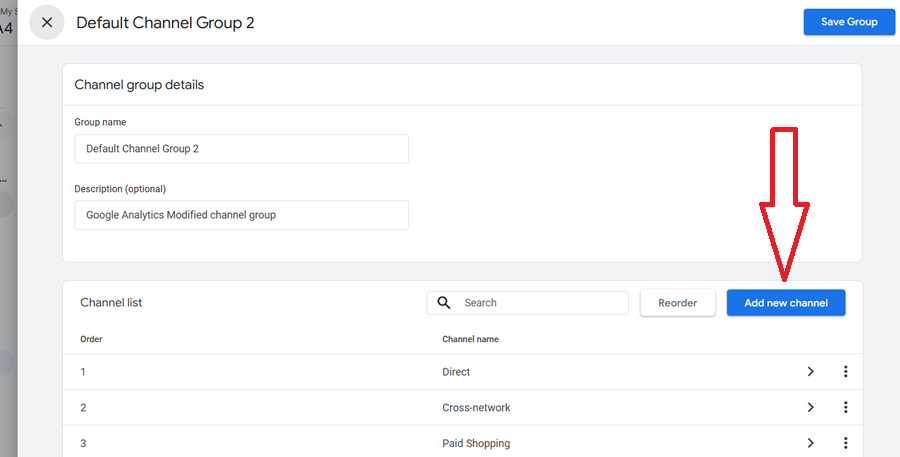
Step-4: Click on the ‘Add new channel‘ button.
Step-5: Name the new channel ‘AI Traffic‘.
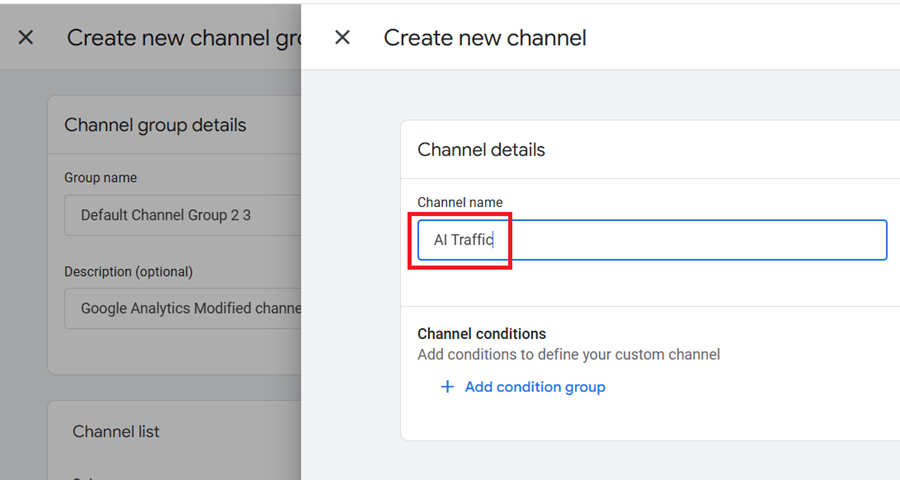
Step-6: Click on the ‘Add condition group‘ button and then add the following condition to define your new custom channel:
Source matches regex
^.ai|..openai.|.copilot.|.chatgpt.|.gemini.|.gpt.|.neeva.|.writesonic.|.nimble.|.outrider.|.perplexity.|.google.bard.|.bard.google.|.bard.|.edgeservices.|.gemini.google.$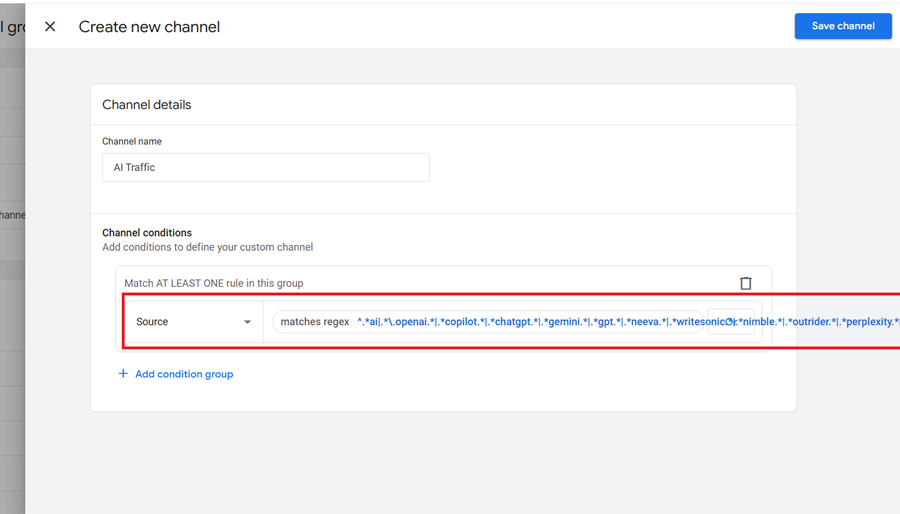
Step-7: Click on the ‘Save Channel‘ button.
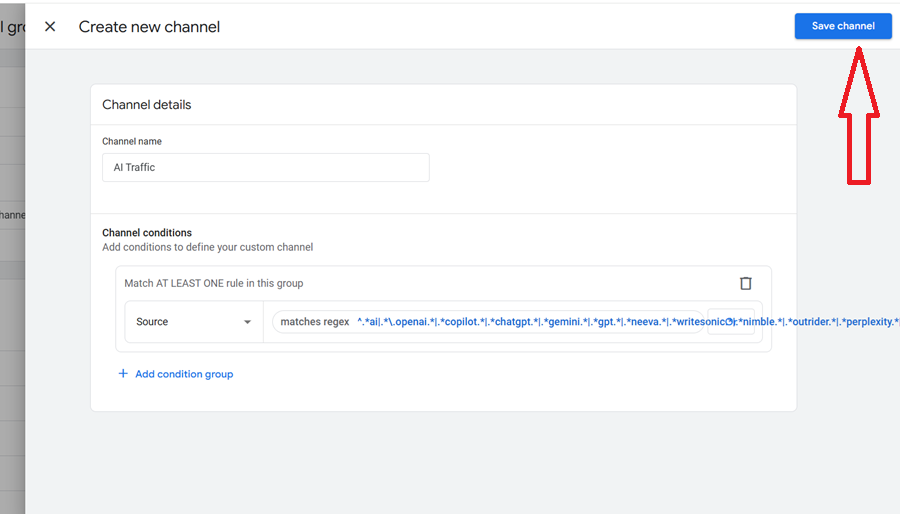
Step-8: Click on the ‘Reorder‘ button and then drag the AI traffic channel just above the ‘Referral’ channel.
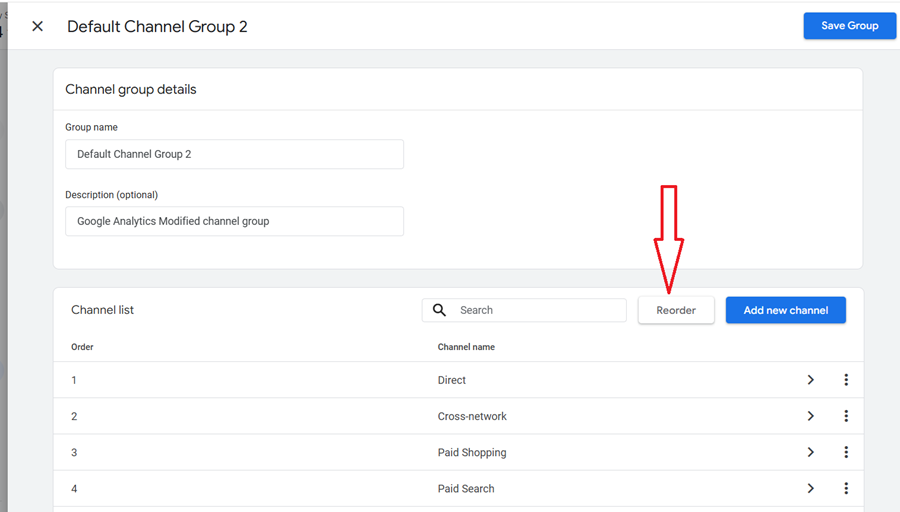
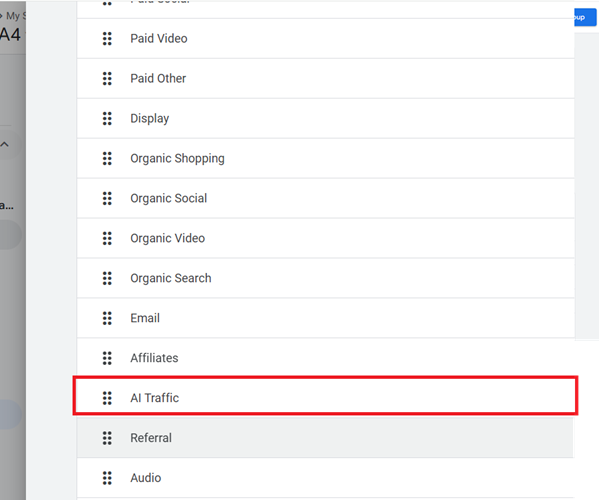
By placing the AI traffic channel above the referral channel, you ensure that AI traffic is correctly attributed before being potentially miscategorized as general referral traffic.
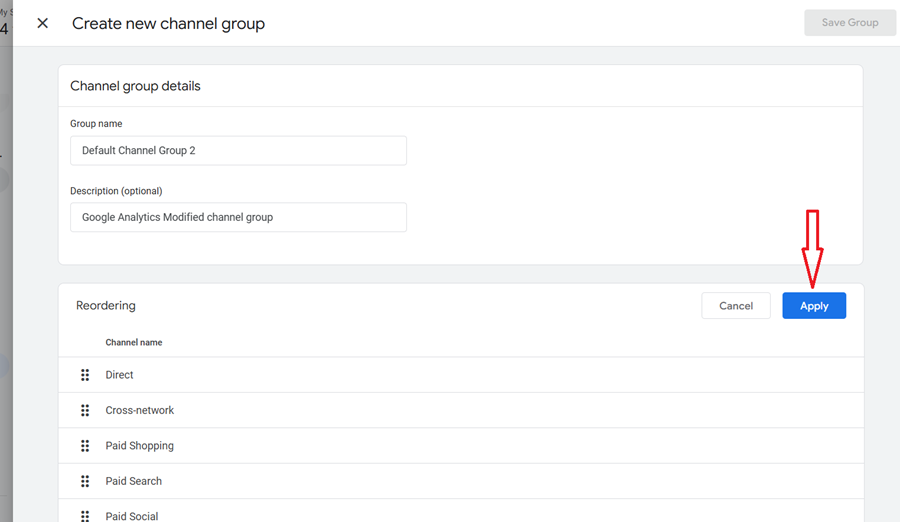
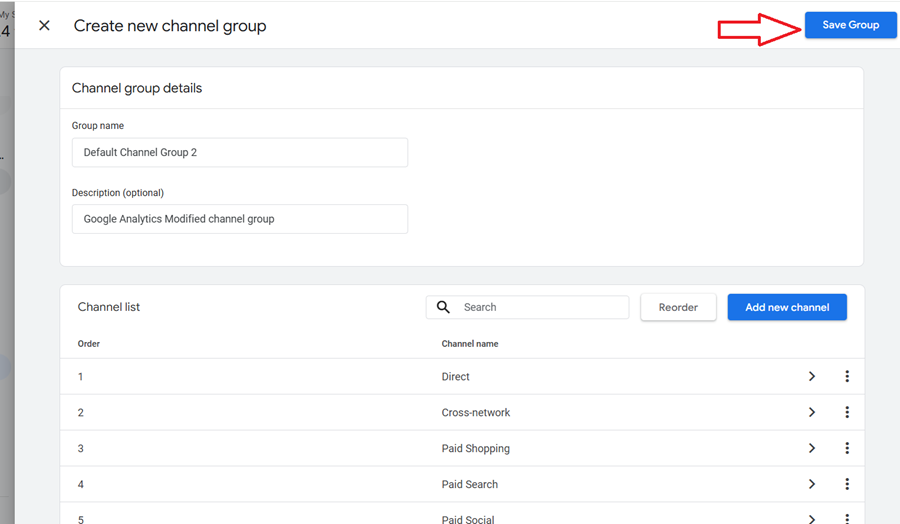
Step-9: Click on the ‘Apply‘ button and then on the ‘Save group‘ button.
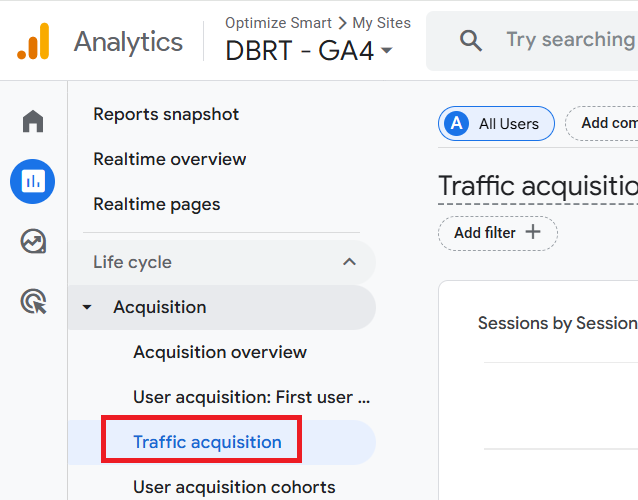
Step-10: Navigate to Reports > Acquisition > Traffic acquisition.
Step-11: Scroll down to the data table and then change the primary dimension to the new channel group you created earlier.
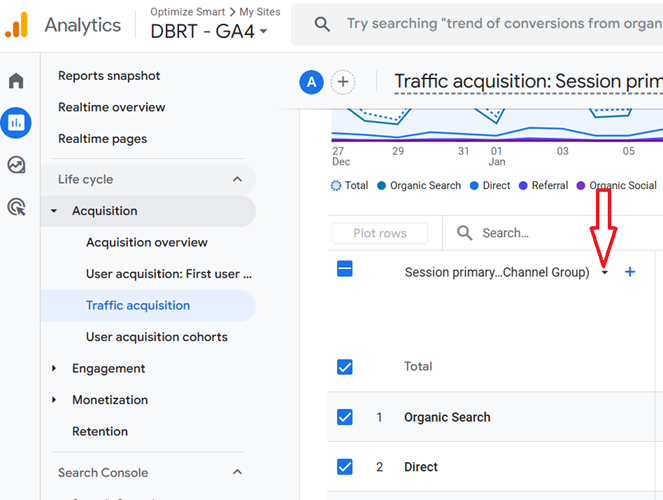
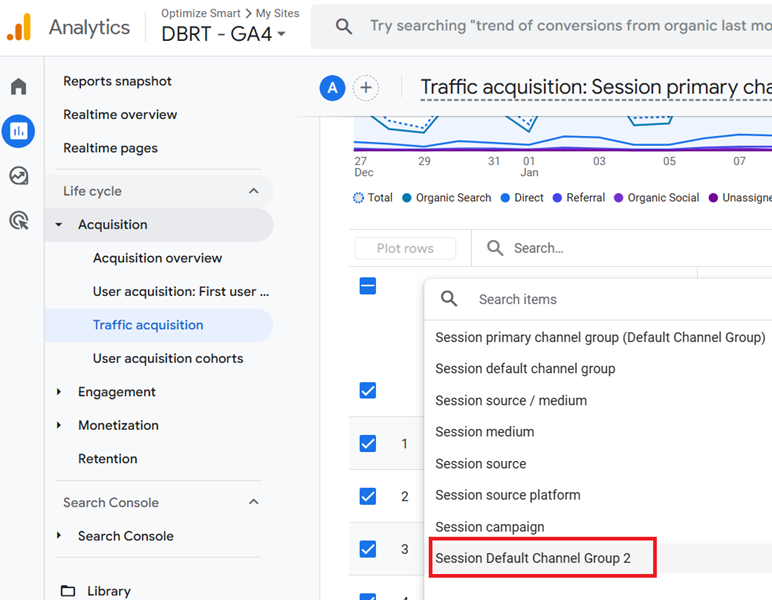
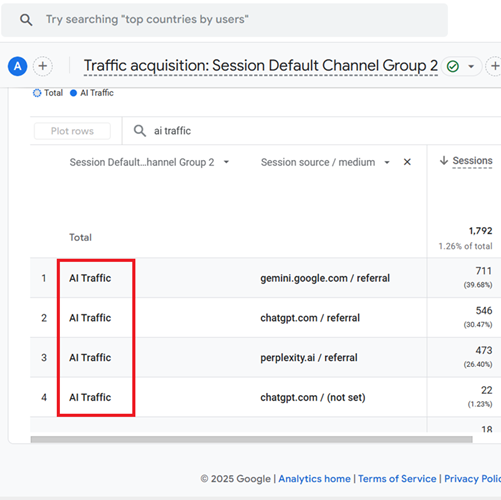
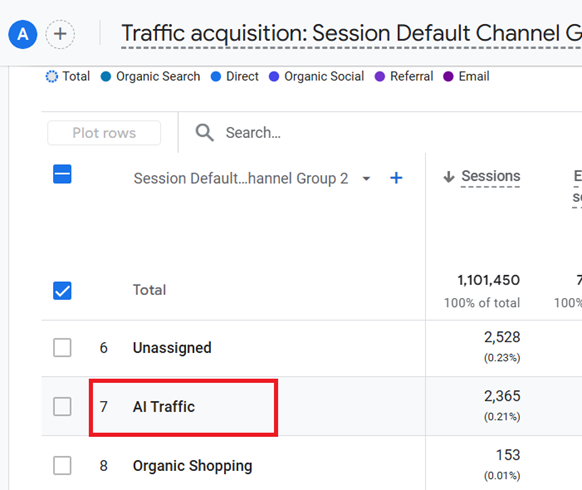
Step-12: If your GA4 property is recording traffic from AI websites, you should see AI traffic being reported via the ‘AI traffic’ channel:
Step-13: Type ‘AI traffic‘ in the search box and press the enter key to filter out the AI traffic channel group.
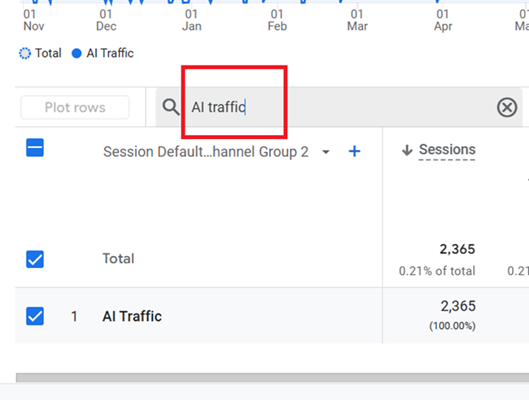
Step-14: Add a secondary dimension to the data table named ‘Session source/medium‘.
You should now see a data table like the one below:
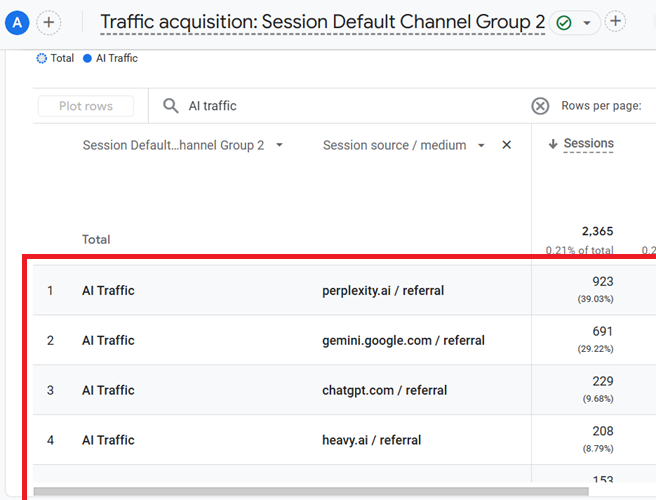
Related Article: Tracking AI Traffic in GA4 BigQuery.
Caveat: Vet your referrer data before including it in your data analysis.
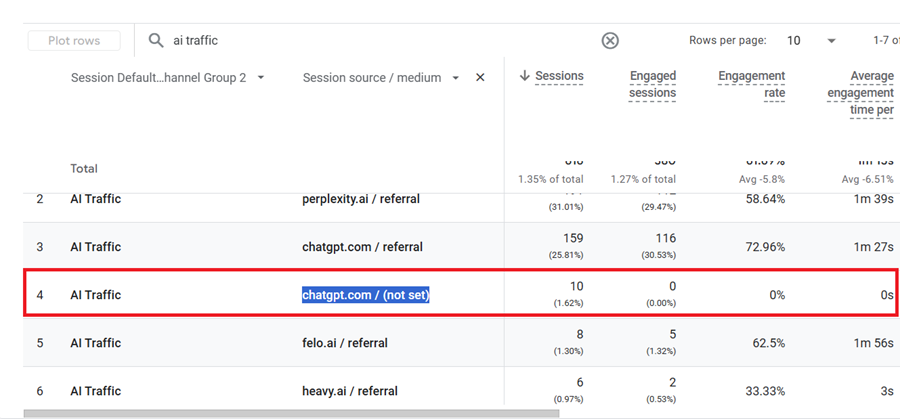
So this is not traffic from chatgpt but BOT traffic, which is easier to spot: 0 engaged sessions, 0% engagement rate and 0 seconds average engagement time per session.
Legitimate traffic from ChatGPT typically has “referral” as the medium.
The (not set) value often indicates malformed tracking data, which bots frequently generate.
This is a solid reminder to thoroughly “vet” referrer data before including it in data analysis.
How AI Traffic should be analysed in GA4?
AI traffic should be analysed in GA4 primarily at the session level rather than the user level.
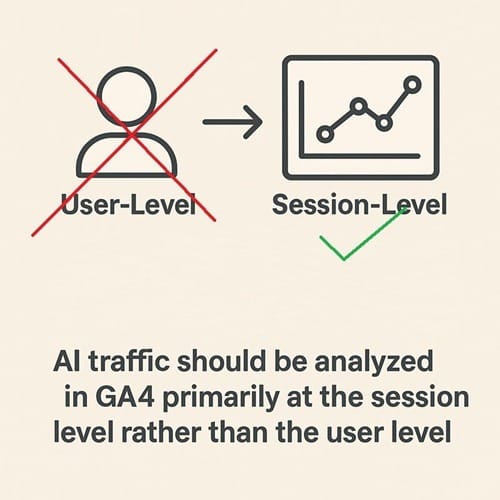
AI systems such as Perplexity or Gemini don’t act like real users, they’re stateless data fetchers.
They don’t log in, store cookies, or maintain a browser session. Each request they make is a standalone interaction.
- No persistent client_id or user_id.
- No cookie continuity.
- No behavioral linkage between requests.
For example,
If Perplexity retrieves three different pages from your website, GA4 will often record three separate sessions, even though all were triggered by one automated process.
This happens because:
>> AI bots like Perplexity do not retain or send persistent identifiers (such as GA4’s client_id cookie) between requests.
>> Each page fetch from the bot is received by your server as an independent HTTP request, lacking continuity or session stitching information.
>> GA4 session logic relies on those persistent identifiers to join hits into sessions. Without them, every new hit is treated as a new session from a “new user,” even if they arrive seconds apart and from the same IP.
This is a well-documented behavior for stateless crawlers and is a key reason to analyze AI-driven traffic at the session level rather than the user level.
This lack of state means user-level analysis becomes meaningless. There is no “user” in the traditional sense.
Since AI traffic lacks continuity and identity, session-level metrics provide a more accurate picture.
They allow you to measure and filter AI interactions without corrupting user behavior analysis.
AI Traffic in GA4 often seems to be more engaged.
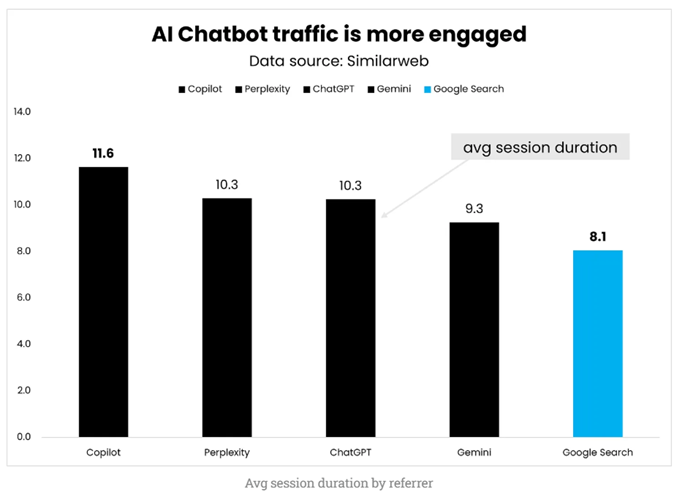
Image Source: https://www.growth-memo.com/p/transactional-ai-traffic-a-study
AI chatbots can interact with your websites like humans.
AI chatbots can interact with your websites like humans and can generate a lot of traffic and user engagement you think are coming from humans.
If AI bots favour your website (like they do in my case), expect an increase in non-human traffic in the coming months.
Several AI tools actively visit, process, and extract information from websites in ways that can resemble human interaction.
For example:
>> Perplexity AI actively browses and scrapes content when users query information.
>> ChatGPT Operator is designed to access the web and interact with websites in a human-like manner.
It is entirely possible that multiple AI agents are scraping, preloading, or interacting with your website at this very moment without your knowledge and you are assuming that it is all human traffic.
These AI systems may load multiple pages, follow links, and keep pages open for extended periods while appearing to be a real user session.
You can validate whether AI systems generate human like engagement by analyzing your traffic data in server logs, GA4, and BigQuery.
Since AI agents don’t behave exactly like humans, they often leave behind patterns in analytics data.
>> Filter for extremely high session durations (e.g., 10+ minutes on average).
>> Look for session paths with excessive page views (e.g., 20+ pages in one visit).
>> Check for navigation patterns. Do some users always land on unexpected pages first or follow unusual click paths?
>> AI bots may load multiple pages faster than a human would. You can validate this by checking for sessions where multiple page requests happen within milliseconds in your server logs.
AI-driven traffic tends to have high engagement but low conversion rate for a reason. It’s not always human traffic.
We don’t really know how much traffic and engagement from AI chatbots are due to human or bot activity.
AI chatbot interfaces often preload websites or fetch data from sources in the background. This means some traffic classified as a “visit” may not come from a human actively clicking a link.
If an AI preloads multiple pages from a website (for ranking or summarization), it could result in higher page views per session without actual user engagement.
Similarweb and other analytics tools often struggle to differentiate between real user sessions and automated prefetching by AI systems.
Besides all engagement metrics reported by analytics tools are wrong because of privacy tools and consent mode skewing the tracking data.
In this case, the only true indicator of traffic quality is the impact on conversions.
Other Articles on GA4.
- Tracking New, Qualified and Converted Leads in GA4.
- Free GA4 training and tutorial with Certification.
- Understanding GA4 Ecommerce Reports (Monetization Reports).
- GA4 Ecommerce Tracking via GTM: Step-by-Step Setup Guide.
- How to see UTM parameters in GA4 (Google Analytics 4).
- GA4 UTM parameters not working? Here is how to fix it.
- How To Use UTM parameters in GA4 (Campaign Tracking).
- How to track AI traffic in GA4.
- Understanding Google Analytics 4 cookies – _ga cookie.
- GA4 (Google Analytics 4) Measurement Protocol Tutorial.
- GA4 Unassigned Traffic: Causes and How to Fix it Fast.
- GA4 Regex (Regular Expressions) Tutorial.
- GA4 Direct Traffic Spike: Common Causes and How to Fix Them.
- gtag.js – Google Tag in Google Analytics 4 and beyond.
- GA4 Scopes – User, Session, Event & Item scopes.
- GA4 Conversion Tracking (Key Events) Tutorial.
- GA4 (not set) - Guide to fixing (not set) issue.

