What is Toll Fraud (also called International Revenue Sharing Fraud)?
Fraudsters trick people or companies into making very expensive calls (or SMS messages) to special international or premium‑rate numbers they control.

The phone companies involved then share the revenue from those pricey calls with whoever owns those numbers, so the attacker gets a cut of every minute your AI Agent spends calling them.
This is called ‘Toll Fraud’.
Toll Fraud is also called “International Revenue Sharing Fraud”.
>> International” because the calls usually go to high‑tariff or premium numbers abroad, where prices are much higher, and controls are weaker.
>> Revenue sharing” because the terminating carrier (the one hosting the premium number) shares part of the call revenue with the fraudster, so both the shady carrier and the attacker profit from your inflated bill.
Understand Outbound toll fraud.
>> An attacker finds a way to trigger outbound calls from your account (stolen API key, weak auth, misconfigured telephony) and directs calls to high‑tariff or revenue‑sharing numbers they control overseas.
>> Your carrier bills you for all these outbound calls; the destination carrier shares part of that revenue with the fraudster (IRSF model), so their direct financial incentive is the outbound spend you incur.
Let us suppose you host a form on your website to collect leads.
As soon as a user submits the forms, they get a call from your voice AI.
Attackers can automatically submit your forms dozens of times, and your AI agent can place dozens of calls to the numbers (premium/revenue‑sharing numbers) owned by attackers.
The attack path is “inbound abuse of the form” but the fraud is on the outbound leg: your system is the one making costly outbound calls to numbers designed to generate revenue for the attacker.
Understand Inbound toll fraud.
Consider the following scenario:
>> You publish a main business number that points to your IVR / voice AI. People call in; that inbound leg is cheap or flat‑rate for you.
>> Your IVR is configured (quite normally) to forward certain menu options or queues to an external destination number, like an after‑hours answering service or “specialist partner line.”
>> An attacker gains access to your PBX/telephony portal or IVR config and silently changes that forward destination to a premium/revenue‑sharing number they control.
>> Now they (or their bots) repeatedly call your main number from low‑cost lines. Each inbound call hits the IVR and is immediately forwarded to the attacker’s premium number, generating expensive minutes on that forwarded leg and revenue share for them, while it still looks to you like “inbound traffic.”
So in an inbound context, the agent is “configured to forward” because that is a normal business feature; toll fraud happens when attackers hijack where those inbound calls are forwarded, turning your inbound entry point into a traffic pump to their premium destinations.
Victims usually discover toll fraud too late.
Victims usually discover toll fraud only when they see an unexpectedly massive bill. You could incur hundreds or even thousands of dollars in a couple of hours.
So you need to check your billing at least once a day.
Use rate limits (per IP, per user, per hour) on your form → call workflow to cap how many calls can be triggered in a short time.
Enable geo‑restrictions in Retell AI.
Retell AI has recently introduced two new settings that can greatly:
#1 Reduce spam and toll fraud by blocking calls originating from countries outside your target market.
#2 Prevents unauthorized international dialing, controls costs, and reduces toll fraud exposure on outbound campaigns.
Allowed Inbound Countries on Retell AI (controlled per phone number).
Use this setting to specific which caller countries are permitted to dial your agent number, as inferred from the caller’s country code; calls from countries not in the list are rejected at the telephony layer.
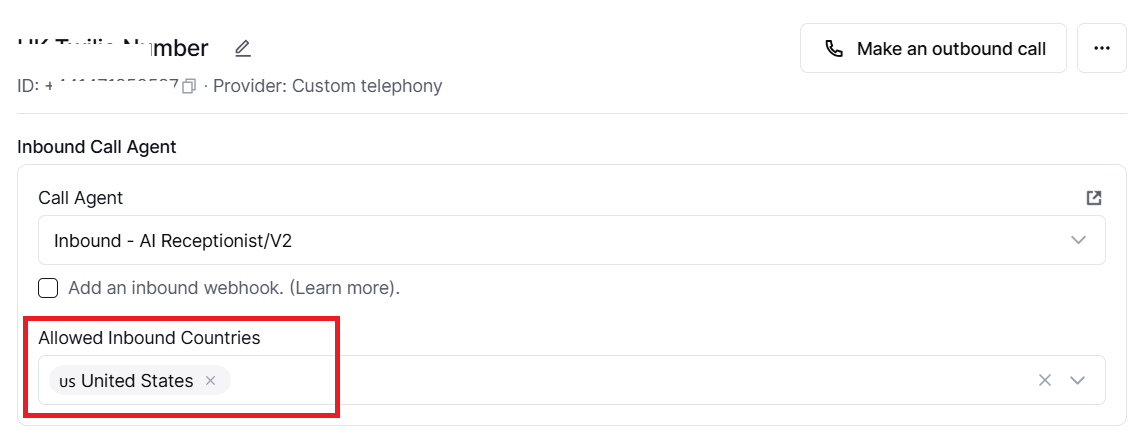
If the inbound allowed countries are not set, inbound calls from all countries are allowed by Retell for that number.
A typical production setup locks inbound to your target market only (for example, ["US","CA"] for North America, or ["GB","IE"] for UK/Ireland) to reduce spam and fraud.
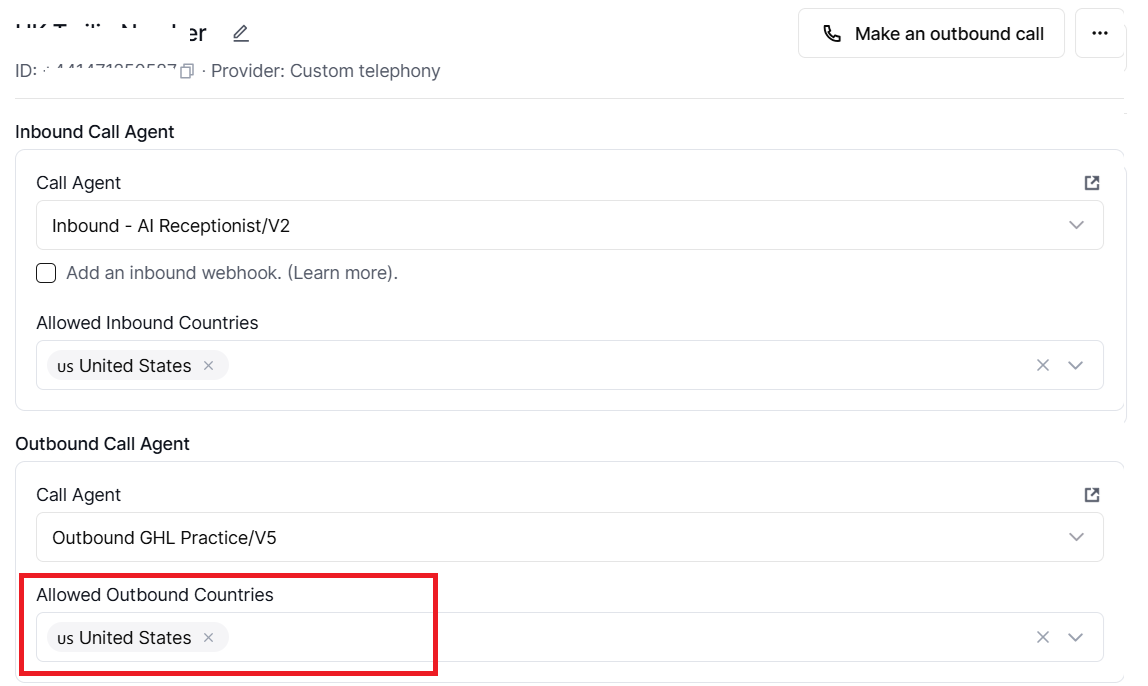
Allowed Outbound Countries on Retell AI (controlled per phone number).
Use this setting to specify which destination countries your agent is permitted to call, based on the destination country code (not the caller's country code). Calls to countries not in the list are blocked at the telephony layer.
Related Articles:
- How to Self Host n8n on Google Cloud - Tutorial.
- How to use APIs in n8n, GoHighLevel and other AI Automation Workflows.
- How to use Webhooks in n8n, GoHighLevel and other AI Automation Workflows.
- What is OpenRouter API and how to use it.
- How to Connect Google Analytics to n8n (step by step guide).
- How To Connect Google Analytics MCP Server to Claude.
- State Machine Architectures for Voice AI Agents.
- Using Twilio with Retell AI via SIP Trunking for Voice AI Agents.
- Retell Conversation Flow Agents - Best Agent Type for Voice AI?
- How to build Cost Efficient Voice AI Agent.
- When to Add Booking Functionality to Your Voice AI Agent.
- n8n Expressions Tutorial.
- n8n Guardrails Guide.
- Modularizing n8n Workflows - Build Smarter Workflows.
- How to sell on ChatGPT via Instant Checkout & ACP (Agentic Commerce Protocol).
- How to Build Reliable AI Workflows.
- Correct Way To Connect Retell AI MCP Server to Claude.
- How to setup Claude Code in VS Code Editor.
- How to use Claude Code Inside VS Code Editor.
- How To Connect n8n MCP Server to Claude.
- How to Connect GoHighLevel MCP Server to Claude.
- How to connect Supabase and Postgres to n8n.
- How to Connect WhatsApp account to n8n.
- How to make your AI Agent Time Aware.
- Structured Data in Voice AI: Stop Commas From Being Read Out Loud.
- How to build Voice AI Agent that handles interruptions.
- Error Handling in n8n Made Simple.
- How to Write Safer Rules for AI Agents.
- AI Default Assumptions: The Hidden Risk in Prompts.
- Why AI Agents lie and don't follow your instructions.
- Why You Need an AI Stack (Not Just ChatGPT).
- How to use OpenAI Agent Kit, Agent Builder?
- n8n AI Workflow Builder And Its Alternatives.
- Two-way syncs in automation workflows can be dangerous.
- Missing Context Breaks AI Agent Development.
- How To Avoid Billing Disputes With AI Automation Clients.
- ChatGPT prompt to summarize YouTube video.
- Avoid the Overengineering Trap in AI Automation Development.

