When I started vibe coding, I had my doubts. My prompts often won't work. There was no structure in place. And the people around me often dismiss my work.
I have been vibe coding for over a year, before it even had a name and have now perfected it to the point where it is now classed as DSL (Domain Specific Language) by ChatGPT for guiding AI Systems in generating SQL queries from plain text.
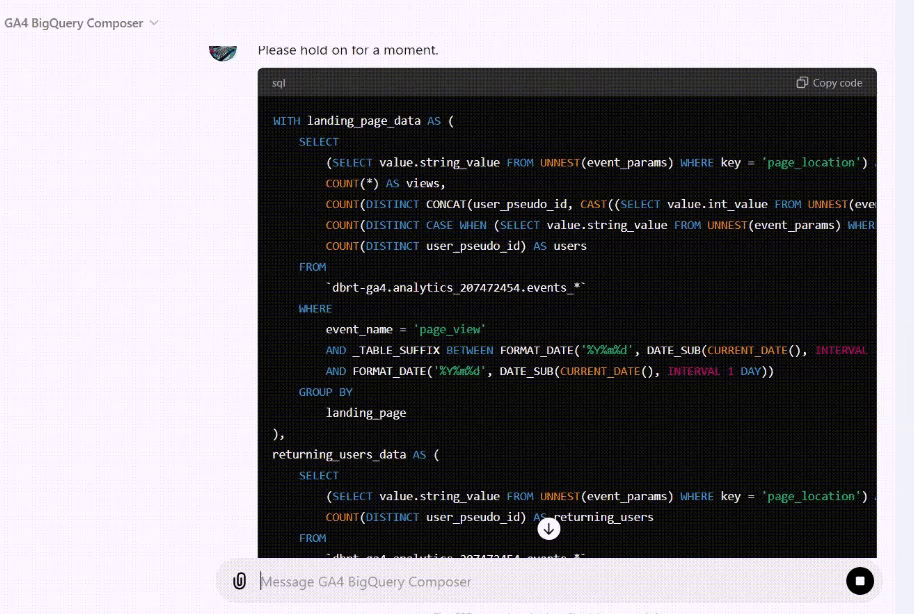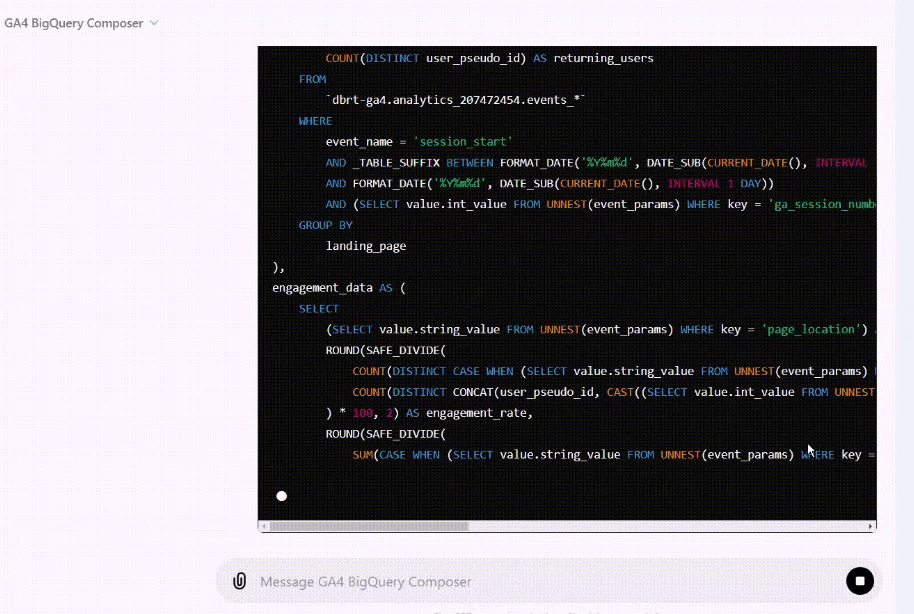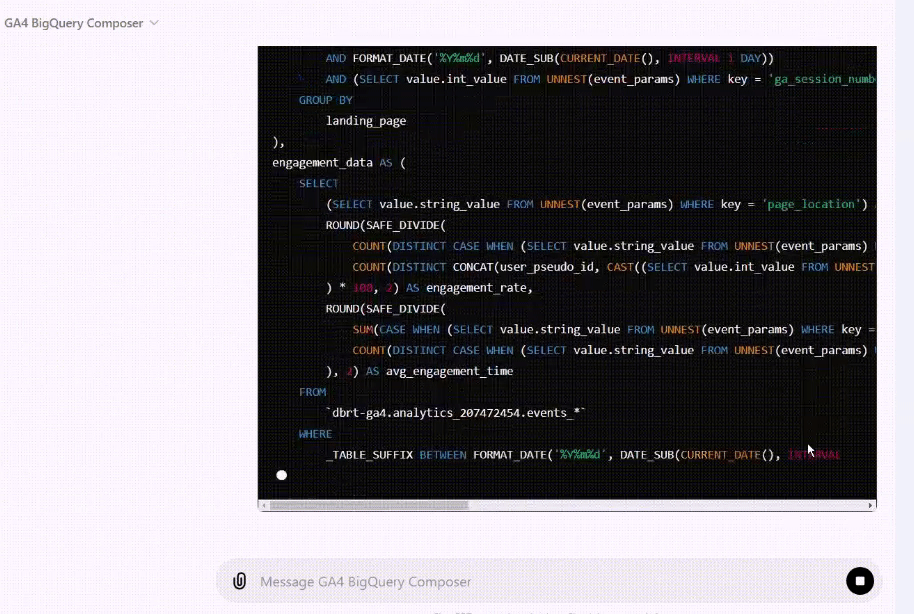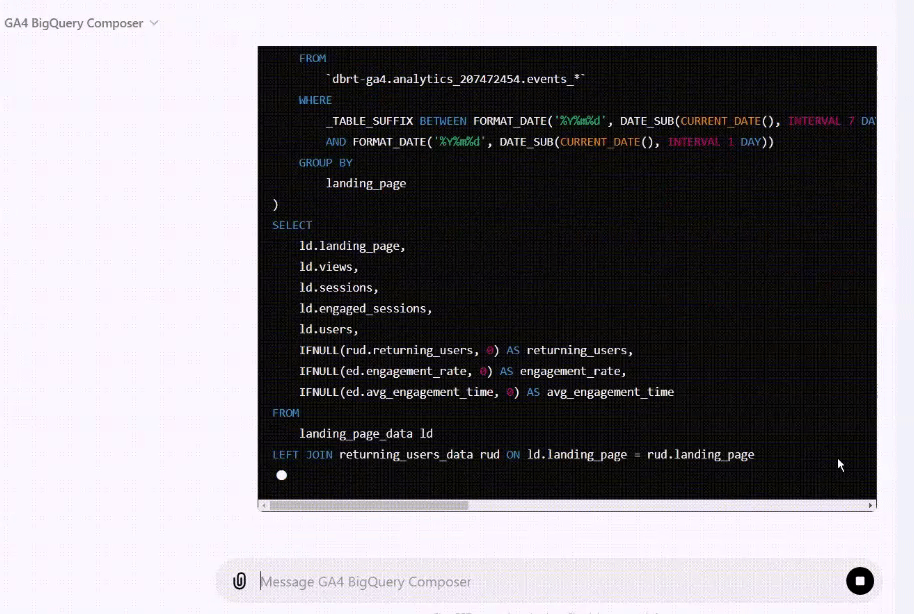
I now teach Vibe Coding for GA4 BigQuery SQL generation to hundreds of students. This isn’t theory I picked up somewhere, it’s hands-on practice, refined through real-world use.
I am not just using Vibe Coding. I have codified it into a language that works consistently for me and for hundreds of others.
I understand it’s a big claim, and I can spend all day convincing you. But the proof is in the pudding.
Wait! What is Vibe Coding?
Vibe Coding is prompt-driven coding. Instead of writing code manually, you describe what you want the code to do in plain language.
Humans describe vibes (intentions) and AI writes the code.
The role of the developer becomes more about guiding, reviewing, and iterating than hand-coding.
Did you hear the word ‘developer’?
If you don’t have a developing background (domain expertise), vibe coding is not meant for you.
May be you have a developing background, but you still struggle with vibe coding. Then it's down to poor prompting skills.
For example, you may have 100 years of experience in Software Engineering. But that does not automatically make you a good vibe coder.
Vibe coding is the practice of crafting structured and precise text-based instructions to guide AI models like ChatGPT in generating accurate and optimised code.
AI is only as good as your input.
The AI you use can not magically produce the desired outcome regardless of advancements in technology if it does not understand what results you are after or if your input is vague, ambiguous or lacks context.
AI systems process text or data literally.
Unlike human communication, where context, past experience and intuition can fill in gaps, AI systems process text or data literally.
They don’t guess or think like humans. They don’t reason about missing details.
They ‘predict’ responses based on your input.
AI doesn’t inherently "know" what you want.
It’s working within the bounds of the information it’s given.
If your input doesn’t articulate a clear intent or goal, the AI can only produce generic or misaligned results.
Vibe Coding Requires Domain Expertise.
Effective vibe coding goes beyond basic instructions. It requires a deep understanding of the specific domain.
This is because AI tools lack contextual awareness and rely heavily on your input.
For example,
AI tools (like ‘ChatGPT’) do not fully understand the GA4 BigQuery Schema, custom dimensions, or event structures. They rely entirely on explicit input from the user.
AI tools often lack knowledge of the underlying logic for calculating specific GA4 dimensions and metrics. This is where human expertise comes into the picture.
Typing a bunch of random text with no predictable syntax and flow is not vibe coding.
A well-designed prompt acts as a programming language for instructing AI to produce structured and reliable outputs, similar to how a software developer writes code.
You should be able to craft precise and effective prompts that scale across various use cases, generate consistent outputs repeatedly and follow a predictable syntax and flow, making them teachable and reusable.
Not every person can use AI tools to develop CODE at a professional level. That's just the harsh reality.

The effectiveness of AI-generated code depends heavily on the clarity and specificity of the input prompt.
Users need to describe the schema, logic and desired output in great detail to achieve meaningful results.
So, while anyone can use AI tools like ChatGPT, not everyone can use them at a professional level for accurate code generation.
Related Articles:
- How to Self Host n8n on Google Cloud - Tutorial.
- How to use APIs in n8n, GoHighLevel and other AI Automation Workflows.
- How to use Webhooks in n8n, GoHighLevel and other AI Automation Workflows.
- What is OpenRouter API and how to use it.
- How to Connect Google Analytics to n8n (step by step guide).
- How To Connect Google Analytics MCP Server to Claude.
- State Machine Architectures for Voice AI Agents.
- Using Twilio with Retell AI via SIP Trunking for Voice AI Agents.
- Retell Conversation Flow Agents - Best Agent Type for Voice AI?
- How to build Cost Efficient Voice AI Agent.
- When to Add Booking Functionality to Your Voice AI Agent.
- n8n Expressions Tutorial.
- n8n Guardrails Guide.
- Modularizing n8n Workflows - Build Smarter Workflows.
- How to sell on ChatGPT via Instant Checkout & ACP (Agentic Commerce Protocol).
- How to Build Reliable AI Workflows.
- Correct Way To Connect Retell AI MCP Server to Claude.
- How to setup Claude Code in VS Code Editor.
- How to use Claude Code Inside VS Code Editor.
- How To Connect n8n MCP Server to Claude.
- How to Connect GoHighLevel MCP Server to Claude.
- How to connect Supabase and Postgres to n8n.
- How to Connect WhatsApp account to n8n.
- How to make your AI Agent Time Aware.
- Structured Data in Voice AI: Stop Commas From Being Read Out Loud.
- How to build Voice AI Agent that handles interruptions.
- Error Handling in n8n Made Simple.
- How to Write Safer Rules for AI Agents.
- AI Default Assumptions: The Hidden Risk in Prompts.
- Why AI Agents lie and don't follow your instructions.
- Why You Need an AI Stack (Not Just ChatGPT).
- How to use OpenAI Agent Kit, Agent Builder?
- n8n AI Workflow Builder And Its Alternatives.
- Two-way syncs in automation workflows can be dangerous.
- Missing Context Breaks AI Agent Development.
- How To Avoid Billing Disputes With AI Automation Clients.
- ChatGPT prompt to summarize YouTube video.
- Avoid the Overengineering Trap in AI Automation Development.

