Navigate
Learn to track events in GA4 (Google Analytics 4) through this step by step guide.
What are GA4 events?
An event is a user interaction with a web page element embedded in a website or mobile app.
The following are examples of web page elements:
- Video.
- Image.
- Button.
- Form.
- scroll bar.
- external link.
- lightbox etc.
The following are examples of user activities that can be tracked as events in GA4:
- Log-ins.
- Clicking on a button.
- Scrolling down the page.
- Downloading a file.
- Loading of a page in the browser window (pageview) etc.
Any user interaction with content on a web page or screen load can be tracked as an event.
In earlier versions of Google Analytics, each event had to be configured separately, either using the global site tag (gtag.js) or Google Tag Manager (GTM).
But in GA4, events are fundamentally different and require a new setup, since many are now preconfigured.
Yes, you heard right!! GA3 can automatically log many events without additional coding or tagging.

Types of events in Google Analytics 4.
There are four categories of events in GA4:
- Automatically Collected Events.
- Enhanced Measurement Events.
- Recommended Events.
- Custom Events.
All of these event categories can be further categorised into:
#1 Web events - These are the events that are recorded only on a website. For example: ‘file_download’, ‘page_view’, ‘scroll’, ‘video_start’, ‘video_progress’, ‘video_complete’, ‘view_search_results’ etc.
#2 App events - These are the events that are recorded only in a mobile app. For example: ‘first_open’, ‘in_app_purchase’, ‘notification_open’, ‘screen_view’ etc.
#3 App+Web events - These are the events that can be recorded across a website and mobile app. For example: ‘first_visit’, ‘session_start’, ‘user_engagement’ etc.
#4 Android events - These are the events that are recorded only on a mobile app installed on an Android device. For example: ‘app_clear_data’, ‘app_remove’, ‘app_store_refund’, ‘app_store_subscription_cancel’ etc.
#1 Automatically collected events.
Automatically collected events are automatically triggered and logged (recorded) by Google Analytics 4 (GA4) on certain pre-defined user activities.
These pre-defined user activities can be (but are not limited to):
- A user clicking on a mobile ad.
- A mobile ad being served on a screen.
- Viewing of a mobile ad.
- Crashing of an app.
- Downloading of a file.
- Launching of a mobile app for the first time.
- Visiting a website for the first time.
- Completing an in-app purchase.
- Loading of a web page.
- Transitioning of a screen on a mobile app.
- Reaching the bottom of a web page.
- Video starts playing.
- Video progression.
- Video ends playing.
- Performing a site search etc.
Note: You don’t need to add any code or tag on your website/app in order to track automatically collected events.
Examples of automatically collected events in GA4.
The following are examples of automatically collected events and their corresponding parameters:
ad_click.
This event is triggered when a user clicks on a mobile ad.
You can supply additional information with this event by using the following parameter ‘ad_event_id‘.
ad_exposure.
This event is triggered when a mobile ad is served on a screen.
You can supply additional information with this event by using the following parameters: firebase_screen, firebase_screen_id, firebase_screen_class, exposure_time.
ad_impression.
This event is triggered when a user views a mobile ad.
You can supply additional information with this event by using the following parameter ‘ad_event_id‘
app_exception.
This event is triggered when an app crashes or throws an error.
For supplying additional information, use the following parameters:
fatal, timestamp, engagement_time_msec
file_download.
This event is triggered when a user downloads a file from a website.
For supplying additional information use the following parameters:
file_extension, file_name link_classes, link_domain, link_id, link_text, link_url
first_open.
This event is triggered when a user launches an app after installing or re-installing it.
For supplying additional information, use the following parameters:
previoius_gmp_app_id, updated_with_analytics, previous_first_open_count, system_app etc.
first_visit.
This event is triggered when a user first visits a website.
in_app_purchase.
This event is triggered when a user completes an in-app purchase.
For supplying additional information use the following parameters:
product_id, price, value, currency, quantity etc
page_view.
This event is triggered each time a web page loads in the browser window.
screen_view.
This event is triggered when a screen transition occurs.
For supplying additional information, use the following parameters:
firebase_screen, firebase_screen_class, firebase_screen_id, firebase_previous_screen etc.
For a complete list of automatically collected events and the supported parameters, check out the official help documentation: https://support.google.com/analytics/answer/9234069

Where to find automatically collected events in Google Analytics 4?
You can find the automatically collected events in the ‘Events‘ report.
Follow the steps below:
Step-1: Navigate to your GA4 reporting view and click on ‘Reports’.
Step-2: Navigate to ‘Engagements’ > ‘Events’ report:
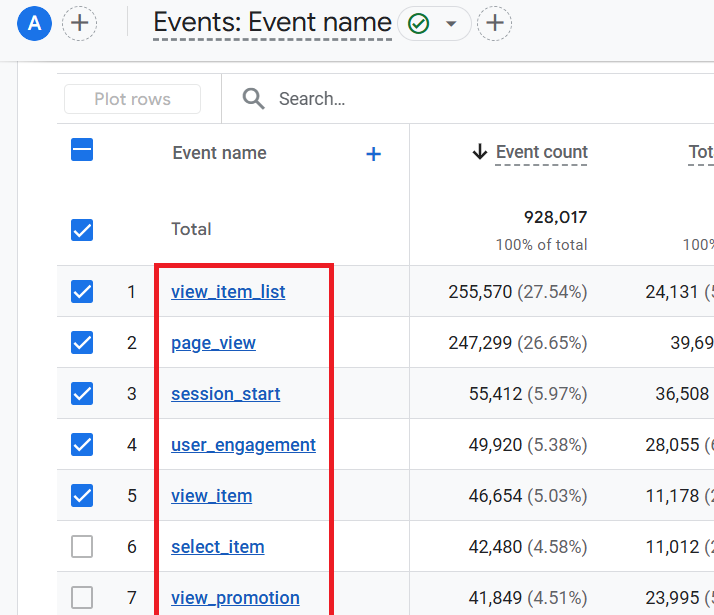
You should now be able to see the complete list of all the logged events (including automatically collected events) in your GA4 reporting view:
#2 Enhanced measurement events.
Enhanced Measurement Events are automatically triggered and logged on certain pre-defined user activities. But the events (excluding ‘page_view’ event) are logged only when you have enabled enhanced measurement in Google Analytics 4.
How to enable enhance measurement events in GA4.
To enable GA4 enhanced measurement events tracking, follow the steps below:
Step-1: Navigate to your GA4 reporting view and then click on ‘Admin’.
Step-2: Navigate to ‘Data Collection and modification’ > ‘Data Stream’:
Step-3: Click on your web data stream:
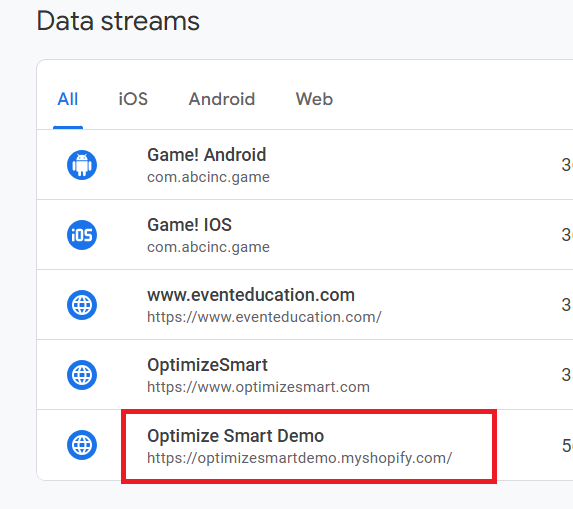
Note: You can enable enhanced measurement only on a web data stream (aka website).
Step-4: Toggle on the switch button next to ‘Enhanced measurement’:
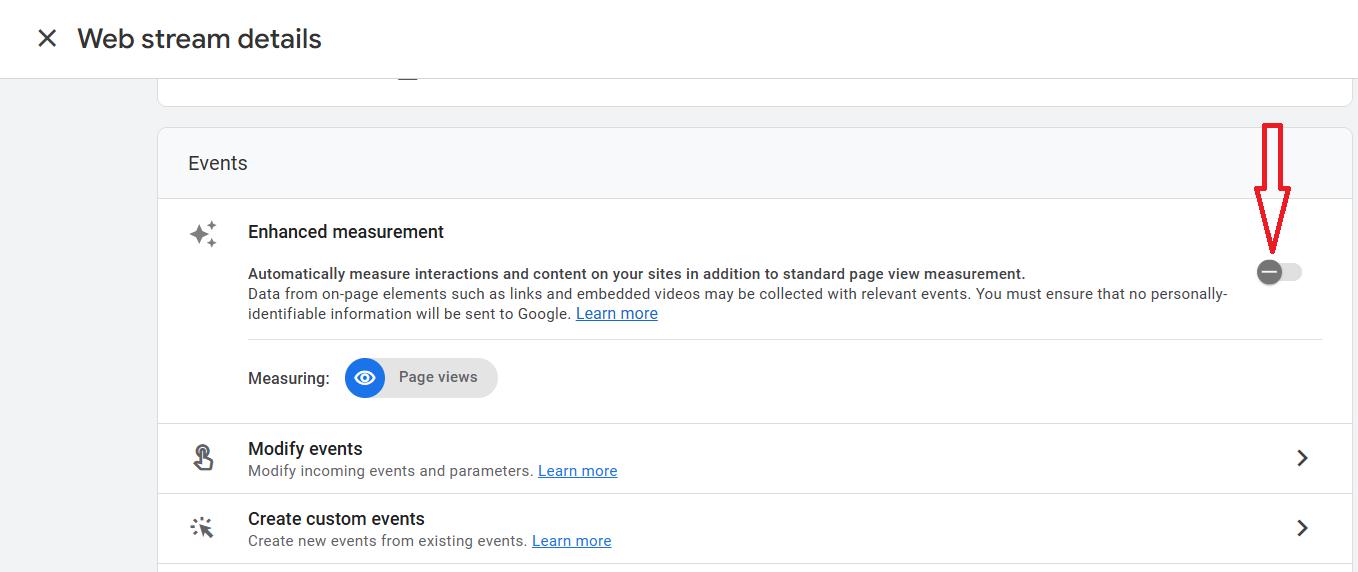
Note: The ‘page views’ events are tracked even if the switch button is off.
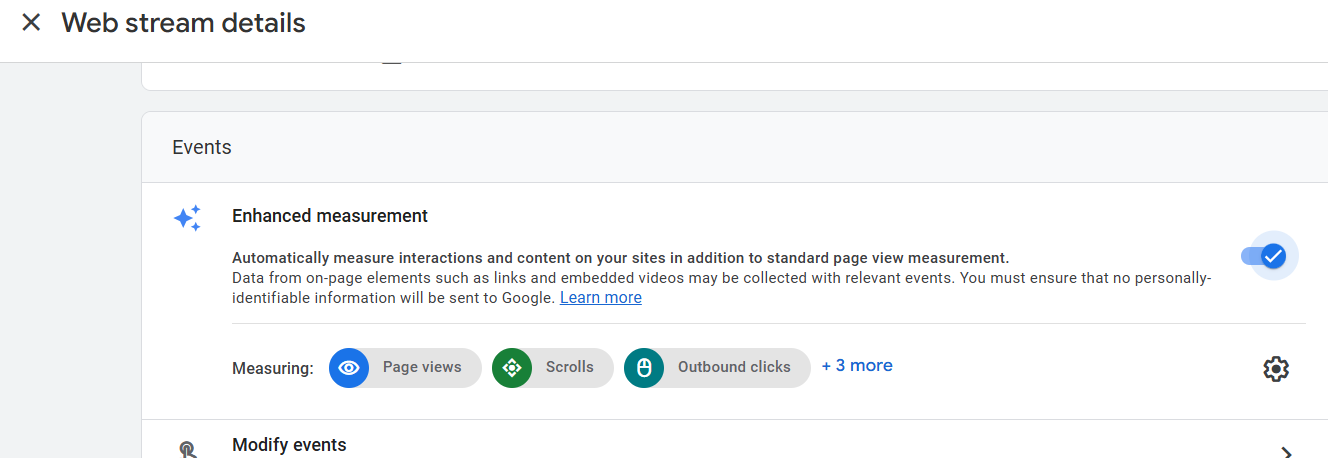
When you switch on the toggle, your GA4 view will also start tracking the following events: ‘Scrolls’, ‘Outbound Clicks’, ‘Site Search’, ‘Video engagement’ and ‘File downloads’:
Step-5: If you want to track only certain enhanced measurement events, then click on the gear icon:
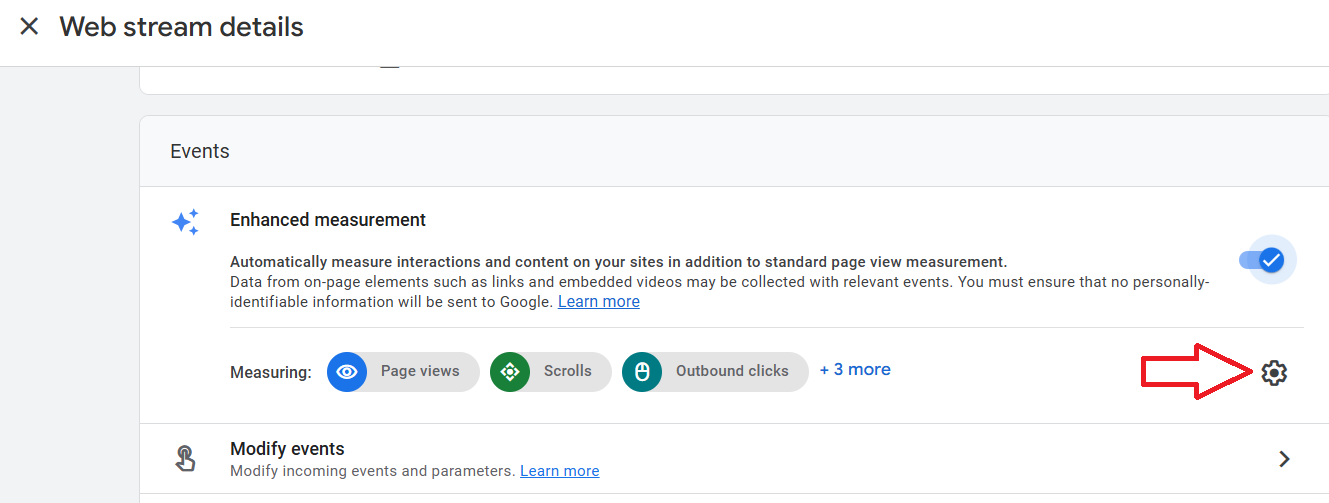
Step-6: Turn off the switch next to the enhanced measurement event you don’t want to track:
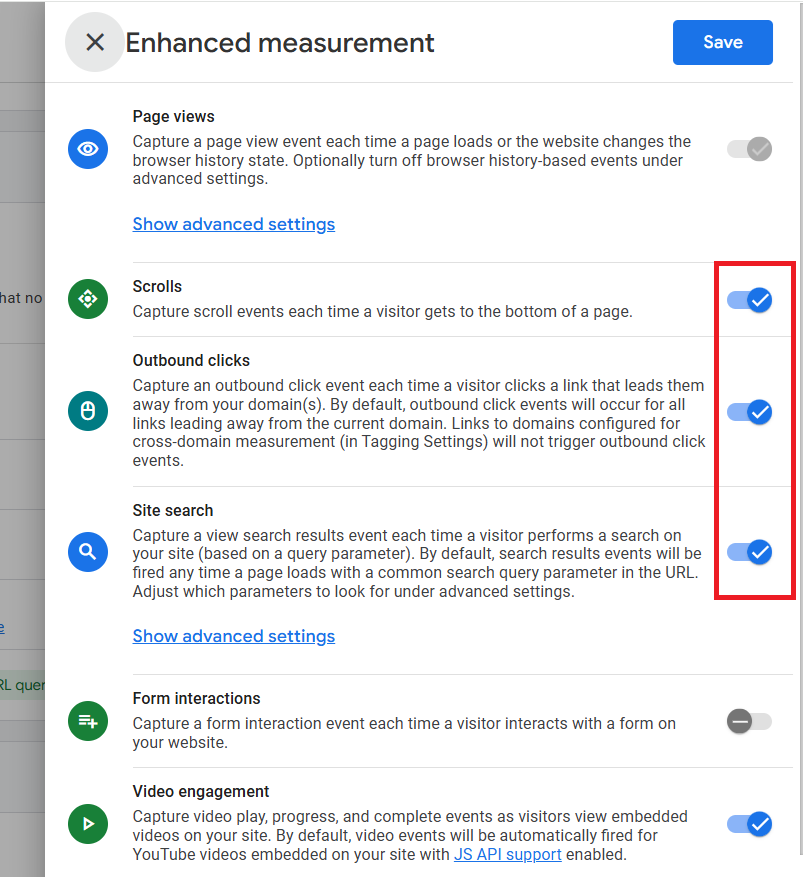
Step-7: Click on the ‘Save’ button, and you are done with enabling the enhanced measurement events.
Examples of Enhanced measurement events in GA4.
The following are examples of enhanced measurement events and their corresponding parameters:
page_view.
This event is triggered each time a web page loads in a browser window.
scroll.
This event is triggered when a user scrolls 90% of a web page.
click.
This event is triggered whenever a user clicks an external link.
You can supply additional information with this event by using the following event parameters:
link_classes, link_domain, link_id, link_url, outbound (boolean).
view_search_results.
This event is triggered whenever a user searches on your website.
video_start.
This event is triggered when a user starts playing an embedded YouTube video.
For supplying additional information, use the following event parameters:
video_current_time, video_duration, video_percent, video_provider etc.
video_progress.
This event is triggered when the user progresses through an embedded YouTube video.
For supplying additional information, use the following parameters:
video_current_time, video_duration, video_percent, video_provider, etc.
video_complete.
This event is triggered when a user completes watching an embedded YouTube video.
For supplying additional information, use the following parameters:
video_current_time, video_duration, video_percent, video_provider, etc.
file_download.
This event is triggered when a user clicks a link to a file.
For supplying additional information, use the following parameters:
file_extension, file_name, link_classes, link_domain, link_id, etc.
Note: You don’t need to add any code or tag to your website in order to track enhanced measurement events.
Check out the official help documentation to learn more about the enhanced measurement events and the parameters each event supports: https://support.google.com/analytics/answer/9216061
How to find enhanced measurement events in Google Analytics 4.
To find the list of all the enhanced measurement events recorded in your GA4 reporting view, follow the steps below:
Step-1: Navigate to your GA4 reporting view and click on ‘Reports’.
Step-2: Naviate to ‘Engagements’ > ‘Events’ report:
You should now be able to see the list of all the enhanced measurement events recorded in your GA4 view.
#3 Recommended events.
Recommended events are the events recommended by Google. They are not triggered and logged automatically unless you manually implement them.
However, for a recommended event to work correctly, you must use the exact same event name and parameter(s) as supplied by Google.
Failing to do so, Google will not recognise your event as one of their recommended events, and your event may either not work the way you want or not get triggered at all.
Google recommends events by business vertical.
For example, Google has recommended a certain set of events and parameters for the following business verticals:
- Retail/ecommerce.
- Travel/Hotel.
- Gaming.
Recommended Google Analytics 4 events examples.
Google recommends the following events for retail and ecommerce apps:
add_to_cart.
This event is triggered when a user adds items to the cart.
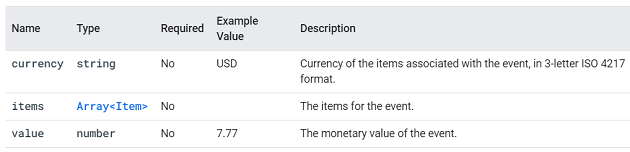
You can supply additional information about this event using the following parameters: currency, items, and value.
begin_checkout.
This event is triggered when a user begins the checkout process.
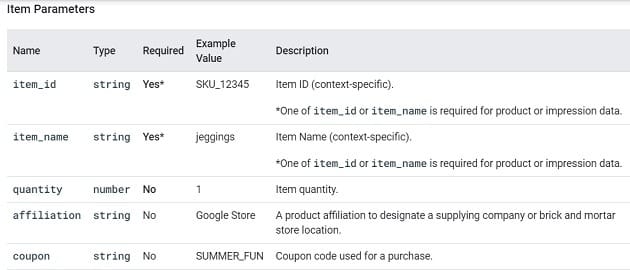
You can supply additional information about this event using the following parameters: coupon, currency, items and value.
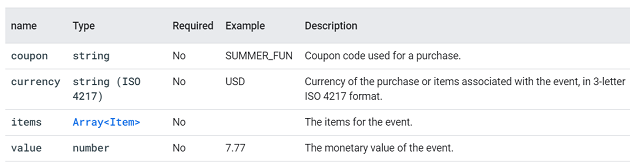
add_payment_info.
This event is triggered when a user submits their payment information.
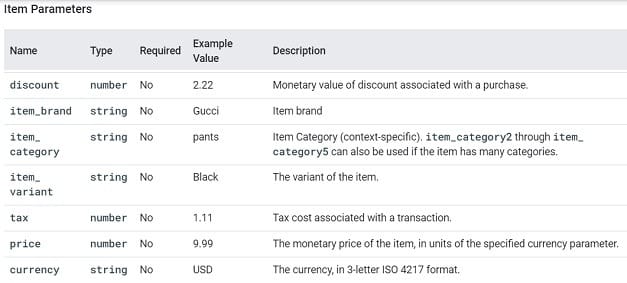
You can supply additional information with this event by using the following parameters: coupon, currency, items, payment_type and value:
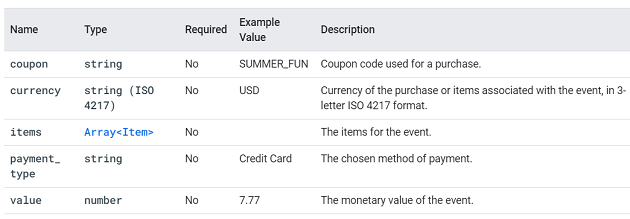
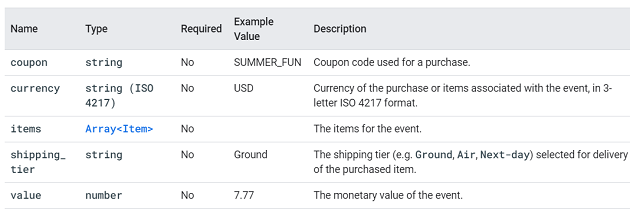
add_shipping_info.
This event is triggered when a user submits his shipping information.
You can supply additional information with this event by using the following parameters: coupon, currency, items, shipping_tier and value.
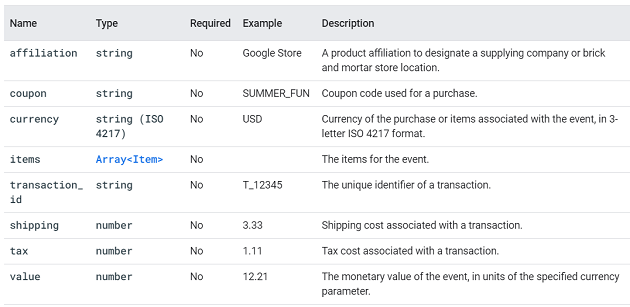
purchase.
This event is triggered when a user completes a purchase of one or more items.
You can supply additional information about this event by using the following parameters: affiliation, coupon, currency, transaction_id etc.
For a complete list of recommended events for retail/ecommerce and the supported parameters, check out the official help documentation: https://support.google.com/analytics/answer/9268036
To learn how to implement these events, refer to the developer documentation and events reference.
Google recommends the following events for travel/hotel-related properties, app or web:
add_to_wishlist.
This event is triggered when a user adds items to a wishlist. Through this event, you can identify popular gift items.
You can supply additional information about this event using the following parameters: currency, items and value.
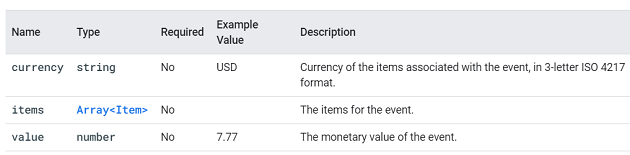
generate_lead.
This event is triggered when a user submits a form.
You can supply additional information about this event using the following parameters: value and currency.
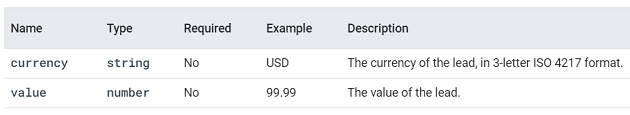
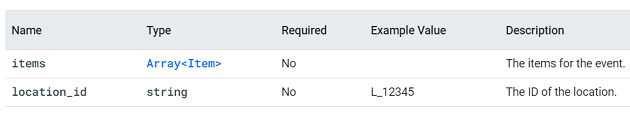
view_promotion.
This event is triggered when a user sees a promotion from a list.
You can supply additional information with this event using the following parameters: items, promotion_id, promotion_name, creative_name, creative_slot and location_id.
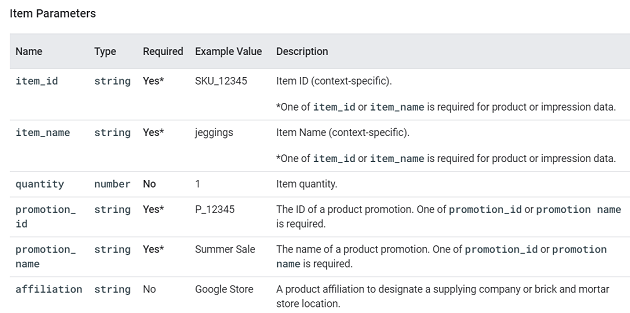
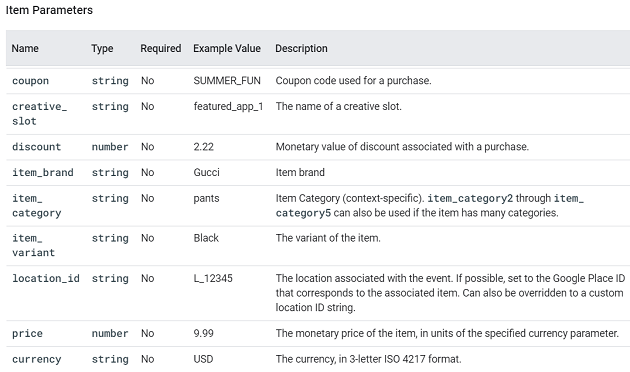
For a complete list of recommended events for travel/hotel and the supported parameters, check out the official help documentation: https://support.google.com/analytics/answer/9267738
To learn how to implement these events, refer to the developer documentation and events reference.
Google recommends the following events for game properties, apps, or web:
tutorial_begin.
This event is triggered when a user begins a tutorial. No parameter is passed with this event.
tutorial_complete.
This event is triggered when a user completes a tutorial. No parameter is passed with this event.
level_start.
This event is triggered when a user starts a new level in the game.
You can supply additional information with this event by using the following parameter: ‘level_name‘.
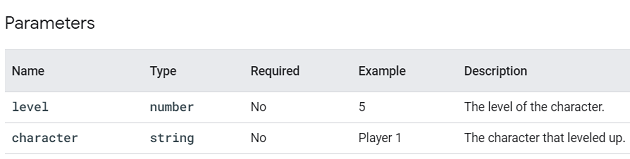
level_up.
This event is triggered when a user levels up in the game.
Through this event, you can understand the overall level distribution of your players and identify levels that are difficult to complete.
You can supply additional information with this event by using the following parameter: character and level.
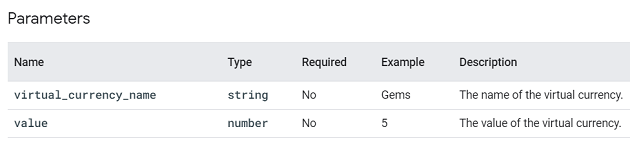
earn_virtual_currency.
This event is triggered when a user has earned virtual currency in the game.
Google recommends that you log this event along with the ‘spend_virtual_currency‘ event to understand your virtual economy better.
You can supply additional information with this event using the following parameters: virtual_currency_name and value.
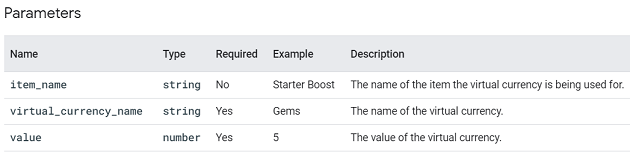
spend_virtual_currency.
This event is triggered when a user has spent virtual currency in the game.
Through this event, you can measure the sales of virtual goods in your app and identify which virtual goods are the most popular.
You can supply additional information with this event by using the following parameters:
item_name, virtual_currency_name and value.
Note: You must supply the ‘virtual_currency_name’ parameter with the event.
level_end.
This event is triggered when a user completes a level in the game.
You can supply additional information with this event using the following parameters: level_name, success.
For a complete list of recommended events for game properties, app or web and the supported parameters, check out the official help documentation: https://support.google.com/analytics/answer/9267565
To learn how to implement these events, refer to the developer documentation and events reference.
Google recommends the following events for all properties (all business verticals, app or web):
sign_up.
This event is triggered when a user has signed up for an account.
A user can sign up via a Google account, email address, etc.
Through the ‘sign_up’ event, you can determine which sign-up methods are the most popular.
You can also use this event to understand the behaviour of logged-in and logged-out users.
You can supply additional information about this event by using the following parameter: ‘method‘.
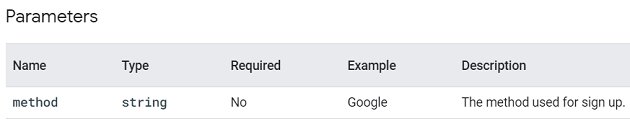
login.
This event is triggered when a user logs in.
A user can log in via a Google account, email address, etc. Through the ‘login’ event, you can determine which methods of login are the most popular.
You can supply additional information about this event by using the following parameter: ‘method‘.
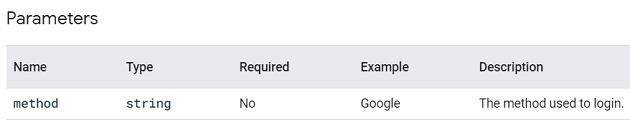
search.
This event is triggered when a user searches for content on your website/app. You can use this event to identify the most popular content on your website/app.
You are required to use the following parameter with this event: ‘search_term‘.
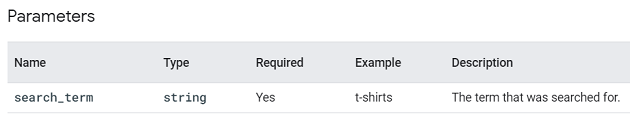
For a complete list of recommended events for all properties (all business verticals, app or web) and the supported parameters, check out the official help documentation: https://support.google.com/analytics/answer/9267735
To learn how to implement these events, refer to the developer documentation and events reference.
#4 Custom events.
Custom events are user-defined events which are used to collect that information which GA4 does not automatically collect.
You can use custom events to track user actions such as button clicks, form submissions, video plays, file downloads, etc.
Google recommends that, before you create a custom event, you ensure there is no automatic, enhanced measurement or recommended event that already provides what you need.
Note: Custom events don’t show up in most standard reports. So you would need to use custom reporting.
You can set custom events and their parameters in two ways:
- Using Global Site Tag (gtag.js) – requires hard coding on the website.
- Using Google Tag Manager (Recommended).
You can create a new custom event from scratch or you can create a new custom event based on an existing event.
Creating custom events from scratch is typically done through Google Tag Manager or directly in the code of your website or app.
Creating custom events based on existing events is simpler and can be done directly within the GA4 user interface.
This method uses an existing event as a foundation, modifying its parameters to create a new event.
A custom event is made up of an event name and one or more event parameters.
Use event parameters to provide additional information about your custom events.
An event parameter is made up of ‘key-value’ pairs where ‘key’ denotes the parameter name and ‘value’ denotes the parameter value.
The parameter name should clearly describe the information being collected.
The parameter value is the actual data associated with that parameter for a specific event occurrence. This value can be a string or an integer.
The parameter name remains consistent across sessions, while the value can change depending on the specific interaction.
Consider the following scenario:
You want to track the price of products purchased by users on your e-commerce website.
- Parameter Name: product_price
- Parameter Value: <The price of the product purchased>
For each ‘purchase’ event, the ‘product_price’ parameter will have a value that reflects the price of the specific product bought by the user.
If User A purchases a product for $50.00, the event parameter would be ‘product_price’: 50.00
If User B purchases a product for $75.00, the event parameter would be ‘product_price’: 75.00
Limits to consider for custom events.
- There is no limit on the number of custom events you can create for a web data stream (i.e., a website).
- There is a limit of 500 distinct events per user per day for mobile app data streams.
- Automatically collected and enhanced measurement events do not count towards these limits.
Setting up GA4 Custom event via Google Tag Manager.
Let’s track clicks on the ‘Buy with Shop Pay’ button as a custom event.
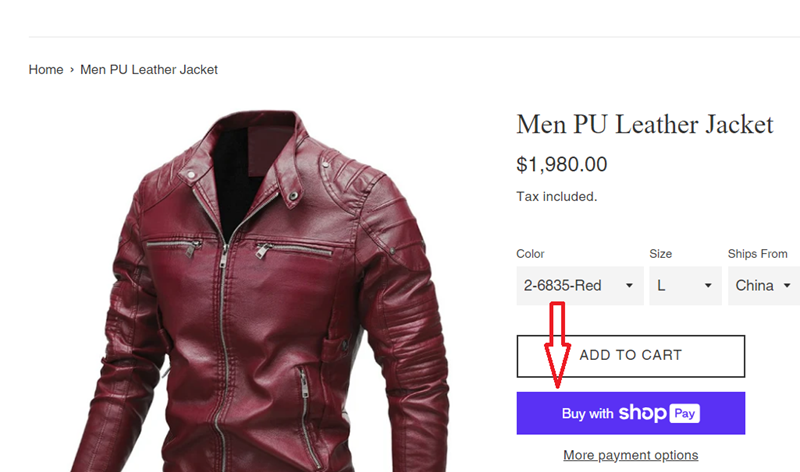
Follow the steps below:
Step-1: Login to your GTM container and create a new trigger with the following configuration:
Trigger Name: Check for click on ‘Buy with Shop Pay’
Trigger Type: Click – All Elements
This trigger fires on
Some Clicks
Fire this trigger when an Event occurs and all of these conditions are true
Click Text contains <enter the click text of your button>
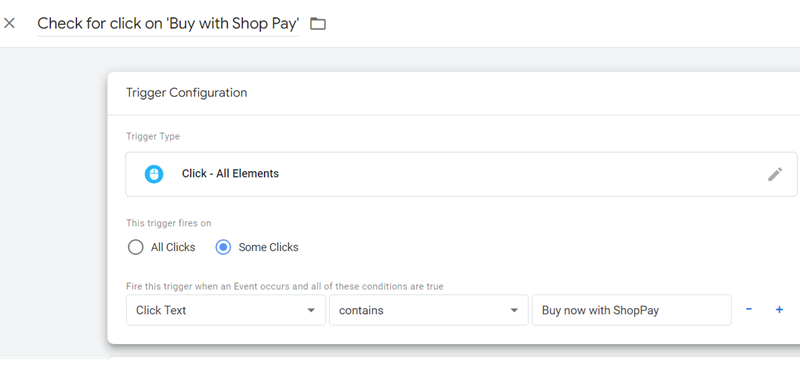
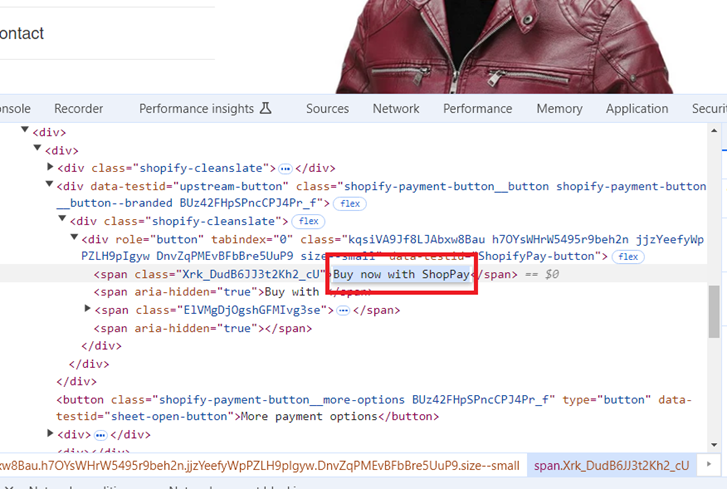
Note: You can determine the ‘click text’ for your button via the developer console:
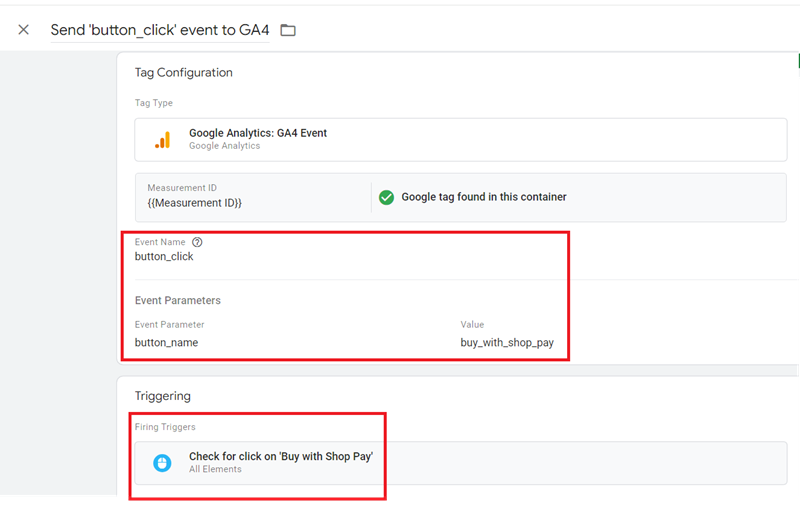
Step-2: Create a new tag with the following configuration, which fires on the trigger we created earlier:
Tag Name: Send ‘button_click’ event to GA4
Tag Type: Google Analytics: GA4 Event
Measurement ID: <your measurement ID>
Event Name: button_click
Event Parameters
- Event Parameter: button_name
- Value: buy_with_shop_pay
Firing Triggers:
Check for click on ‘Buy with Shop Pay’
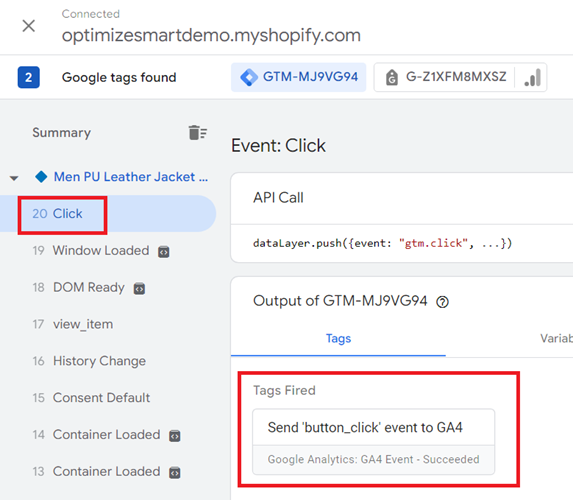
Step-3: Preview your GTM container and click on the ‘Buy with Shop Pay’ button embedded on your website.
You should now see the tag ‘Send ‘button_click’ event to GA4’ fired for the ‘click’ event in Google Tag Assistant:
Step-4: Navigate to the DebugView report in your GA4 property and look for ‘button_click’ event:
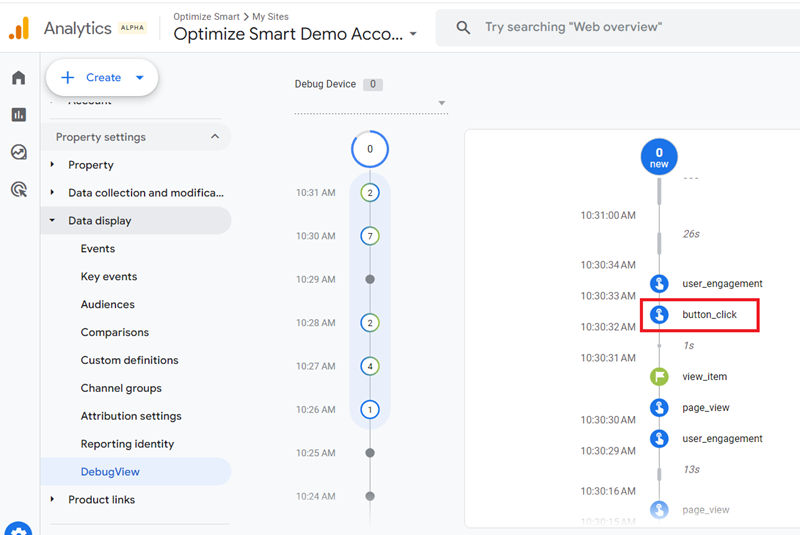
Step-5: Find and click on the ‘button_name’ parameter:
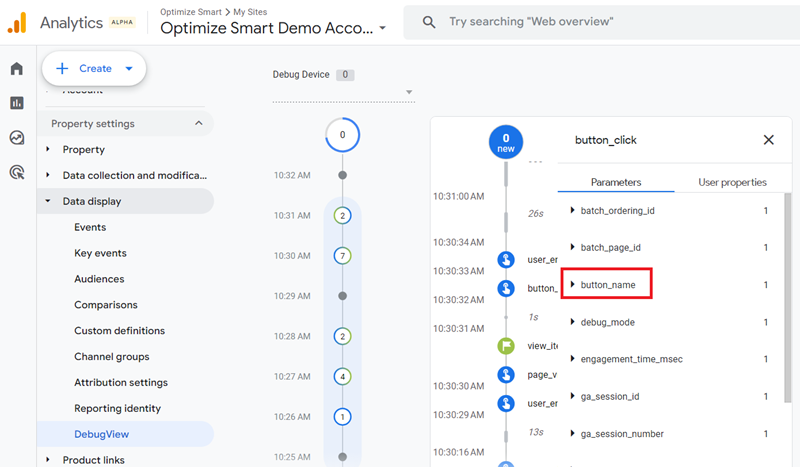
You should now be able to see the value of ‘buy_with_shop_pay’:
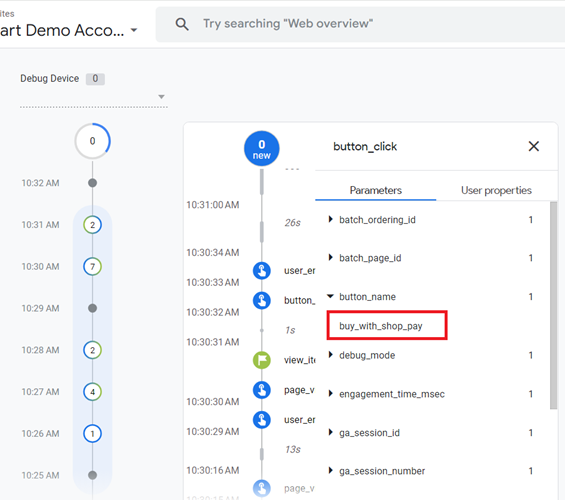
This proves that our custom event is working as expected.
Step-6: Navigate back to your GTM container and then publish it.
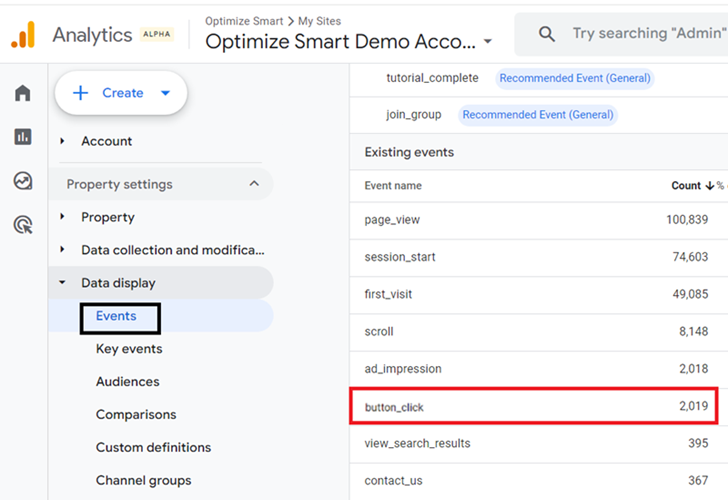
Step-7: Once 24 hrs have elapsed, navigate to the ‘Events’ report in your GA4 property to see the number of times your custom event was triggered:
Step-8: Turn on the toggle button next to your custom event to mark it as a ‘key event’ (optional):
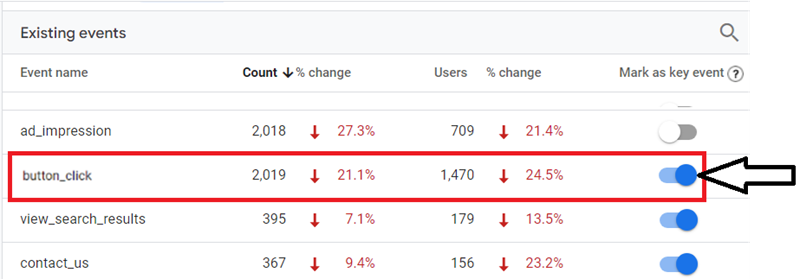
Note: Instead of the toggle button, click on the star button to mark an event as a key event.
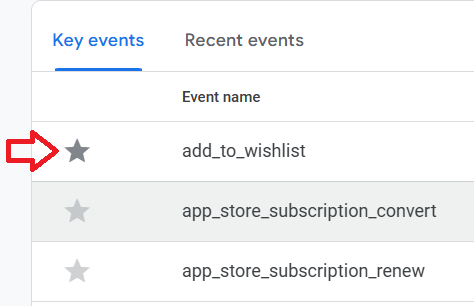
That’s how you can set up custom events from scratch via Google Tag Manager.
Setting up GA4 Custom event from a logged event.
In GA4, you can also create a custom event from an existing event (i.e. logged event).
Suppose you want to track large purchases in GA4 and then target high-value purchasers in Google Ads.
When a user makes a large purchase, you fire the ‘large_purchase’ event.
Follow the steps below to setup the ‘large_purchase’ custom event from a logged event named ‘purchase’:
Step 1: Decide what a large purchase means for you. Let us define a large purchase as any purchase with a value of at least $500.
Step-2: Navigate to GA4 Admin > ‘Data Display’> ‘Events’ > ‘Custom Configuration’ > ‘Custom Events’:
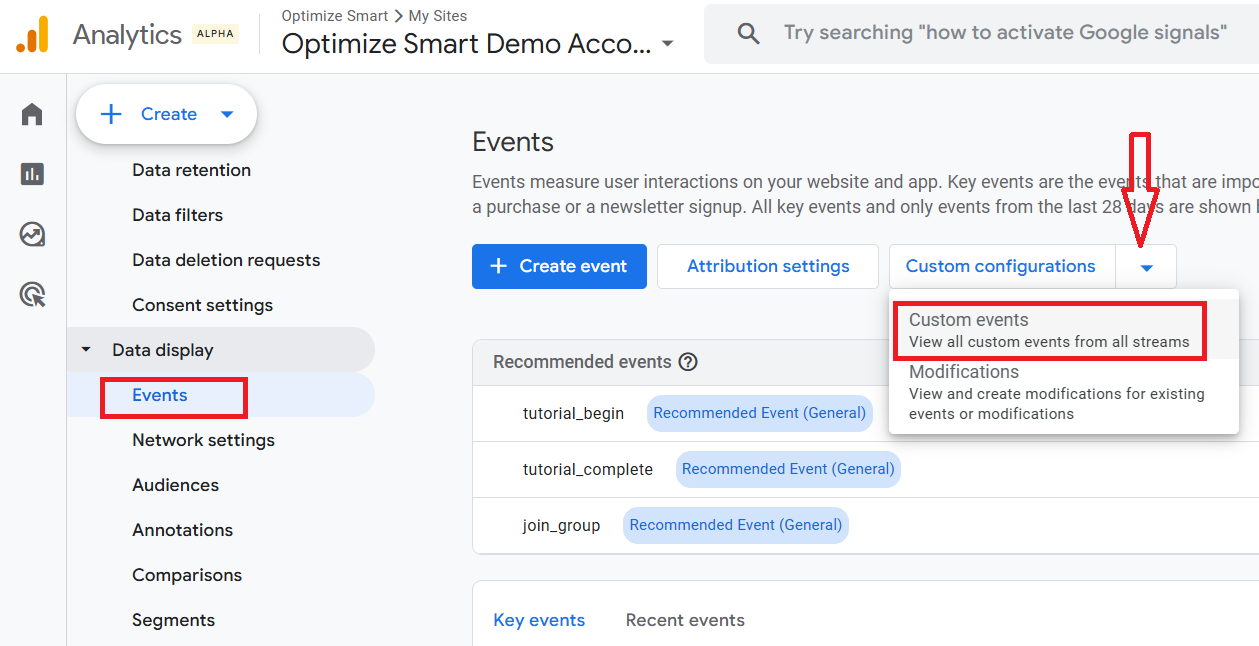
Step-3: Click on the ‘Create’ button to create a new custom event named ‘large_purchase’ using the following configuration and then click on the ‘Create’ button:
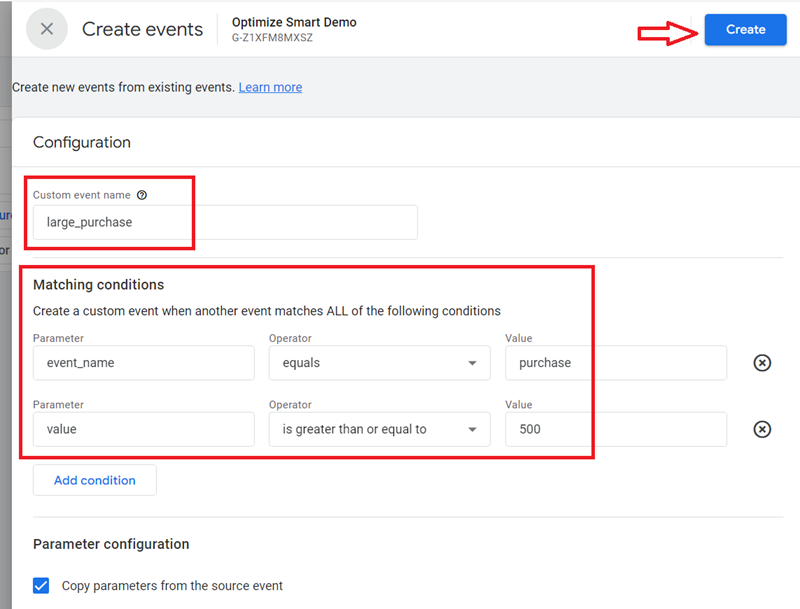
You can use similar logic to track different categories of website purchases.
Note: Do not type the currency symbol in the ‘value’ field.
Step-4: Wait for around 24 hours and then navigate back to the ‘Events’ report. If a large purchase was made on your website, then you should see the ‘large_purchase’ event logged in your ‘Events’ report:
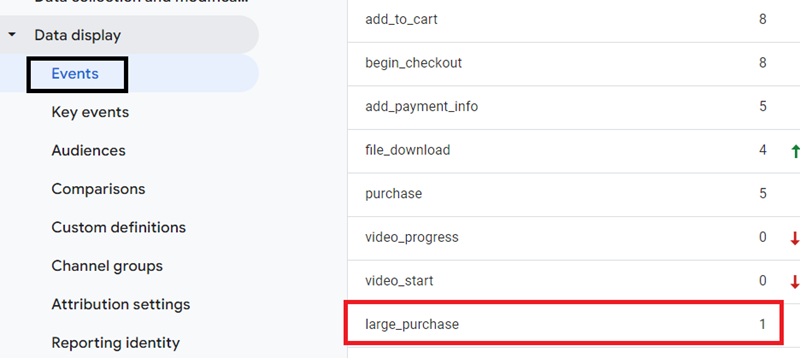
Step-5: Create a new audience in your GA4 property, which is made up of users who made a large purchase. Name this audience ‘High Value Purchasers’.
Step-6: Use this audience as a remarketing audience in Google Ads to target high-value purchasers.
That’s how you can set up a custom event based on an existing event.
Modifying/Renaming Events in GA4.
You can rename events in GA4 in the following situations:
#1 Make an existing event (aka logged event) name more descriptive.
#2 Fix a typo in the event name.
Important points to keep in mind before you rename GA4 events.
#1 Event names are case sensitive. For example, ‘scroll_90’ and ‘Scroll_90’ are distinct events.
#2 Event names must start with a letter. You can use only letters, numbers, and underscores. You can not use spaces.
#3 As event names are case sensitive, it is a best practice to use only lowercase letters when renaming an event.
#4 GA4 allows event names to include both English and non-English words and letters. However, it is a best practice to use only English words as non-English words because some data analysis tools or dashboards might not render non-English characters correctly, leading to display issues.
#5 Use underscores to separate words in your event names.
#6 Keep event names under 40 characters. If you rename a GA4 event with a new event name exceeding 40 characters, it will no longer be processed.
#7 When you rename an existing event, the change does not apply to historical event data.
#8 You can rename up to 50 existing events.
#9 It can take an hour or more before the changes to the event name take effect in your GA4 reports. However, you can see the renamed event instantly in the real-time reports.
#10 Events sent via measurement protocol can not be renamed through the GA4 user interface.
#11 Before you rename an existing event make sure that your new name is not a reserved name.
#12 You will need the ‘Editor or Administrator’ permission to rename events in a GA4 property.
#13 Be careful when renaming events that are already marked as ‘key events’. If you rename an event that is already marked as a key event, that event will no longer be treated as a key event.
How to modify/rename events in GA4.
Let’s rename the automatically collected event called ‘scroll’, which is automatically triggered when a user scrolls down 90% of a web page.
The event fires only once per page view, even if the user scrolls multiple times. It does not track intermediate scroll depths (like 25%, 50%, 75%).
If a user is new to GA4, they won’t necessarily understand from the name ‘scroll’ that this event is, by default, captured at the threshold of 90%.
We can fix this problem by renaming the ‘scroll’ event to ‘scroll_90’.
Follow the steps below:
Step-1: Navigate to the admin section of your GA4 property.
Step-2: Click on ‘Events’ under ‘Data Display’:
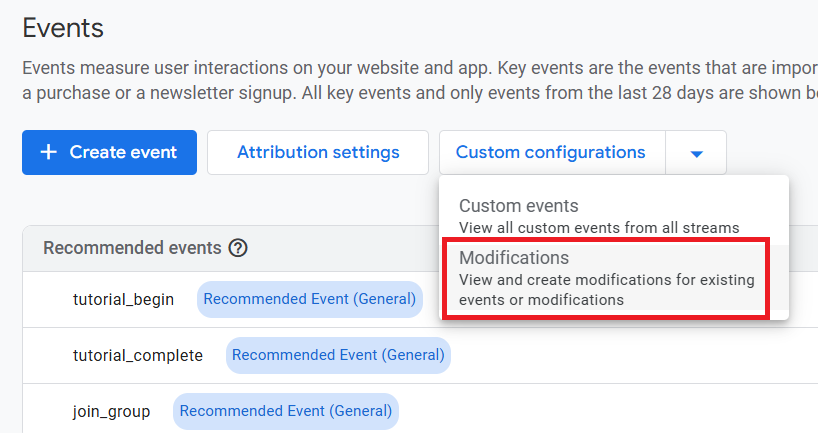
Step-3: Navigate to ‘Custom Configurations’ > ‘Modifications’:
Step-4: Click on the ‘Create’ button, use the following configuration to modify the scroll event and then click on the ‘create’ button again.
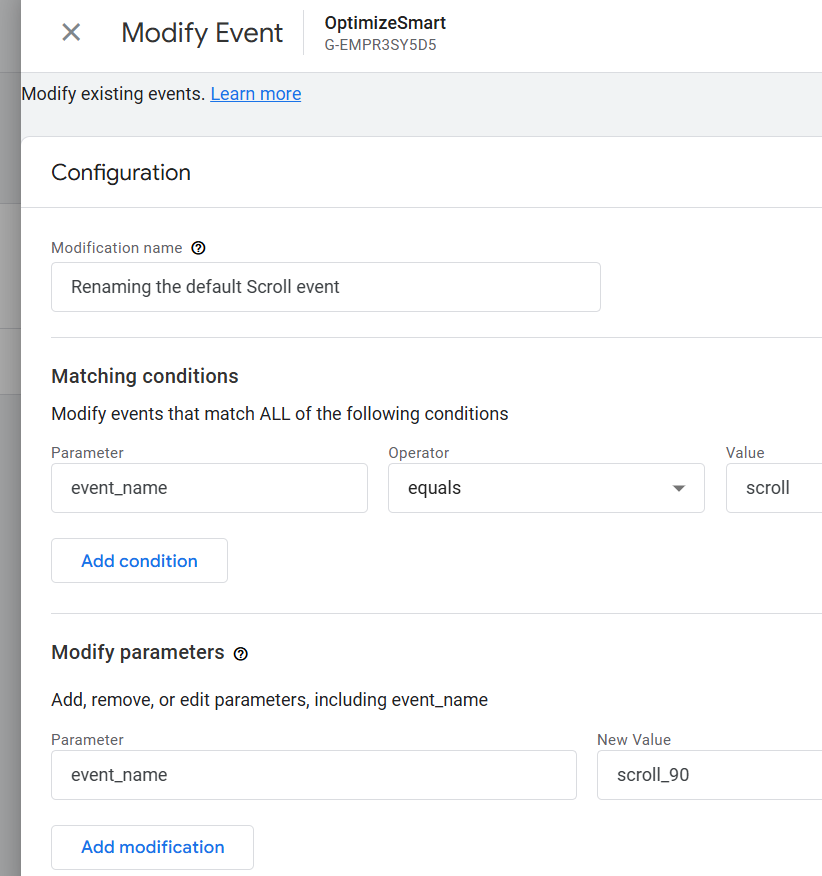
Note: Modification name is for internal use only. It won’t appear in your GA4 reports.
Step-5: Navigate to your website and scroll down 90% or more of a web page.
Step-6: Navigate to the ‘Real-time’ report in your GA4 property.
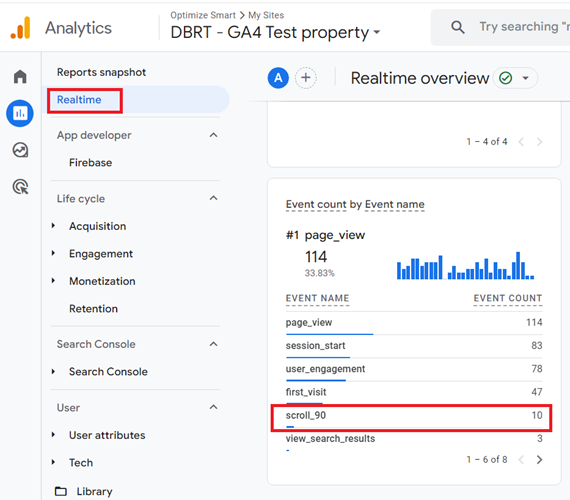
Note: If you don’t see the new event name, then wait for an hour or so before resuming your testing.
That’s how you can modify/rename events in GA4.
Avoid renaming events in GA4.
Renaming events in GA4 is not recommended, as it can skew your analytics data for good.
Renaming a GA4 event does not retroactively change the historical data. The new event name will only apply to data collected after the change.
Your historical data will remain under the original event name.
This means you will have two sets of data: one for the original event name and another for the renamed event, starting from the time of the change.
You will end up with two data sets for the same user interaction, but under different event names.
It will become harder to track the performance of a specific event over time when the data is split across multiple names, especially if you are not aware of the name change.
You will have to merge the old and new event names manually. GA4 does not automatically merge data from renamed events.
Your reports could become misleading to users unaware of the name change.
If you rename a GA4 event with a new event name exceeding 40 characters, it will no longer be processed.
Instead of renaming an event, create a new event.
Note: If you rename an event that is already marked as a key event, that event will no longer be treated as a key event. If you modify event parameters but do not change the event name, the event remains a key event.
The Events report in Google Analytics 4.
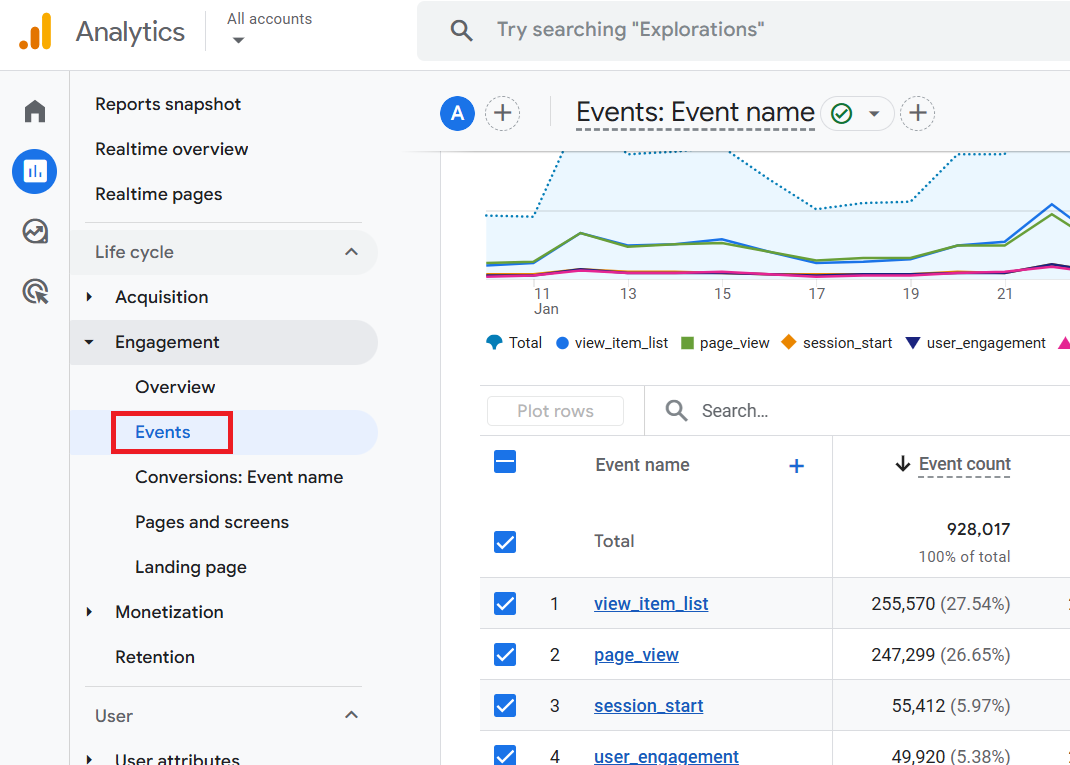
Through the ‘Events’ report, you can do the following:
- See the list of all the logged events in your GA4 reporting view.
- Determine how many times each logged event was triggered.
- Determine the % change of count for each logged event.
- Determine the total number of users who triggered each logged event.
- Determine the % change of users for each logged event.
- Search for a particular event.
- Download the ‘Events‘ report as CSV.
- Sort the ‘Event Name‘, ‘Count‘ and ‘Users‘ metrics in ascending or descending order.
- Get a detailed report for a logged event.
Click on an event name to get a detailed report:
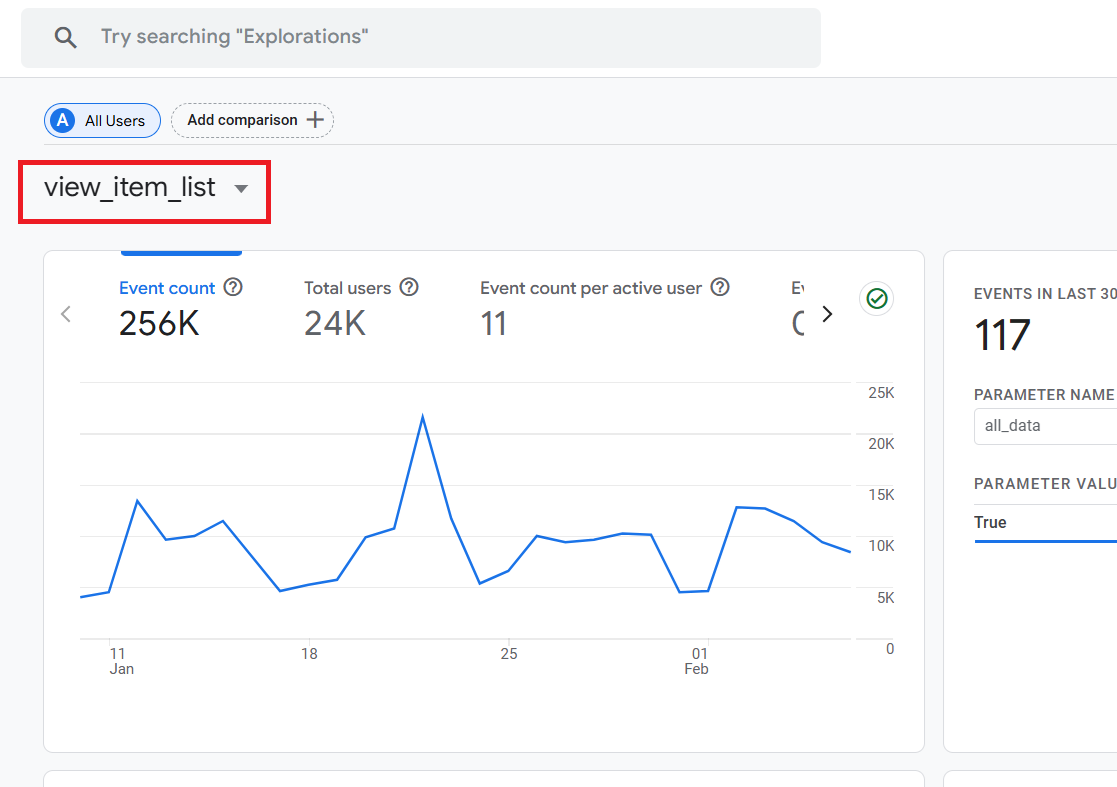
What are the event parameters in GA4?
You can send additional information about an event in Google Analytics 4 via one or more parameters.
There are three types of event parameters:
#1 Automatically Collected Parameters – GA4 automatically collects these parameters.
#2 Custom Parameters – These are the parameters you manually send along with an event.
#3 User properties – They are like user-scoped custom dimensions of Universal Analytics. They are used to describe the attributes of your website/app users.
Event collection limits.
GA4 has limitations on collecting events per property. Once your event or event parameter exceeds these collection limits, they are no longer recorded by GA4.
Please keep the following limitations in mind while setting up custom events:
Avoid analysing the GA4 Event data until the full three days have elapsed.
That means no data analysis for today and the last two days. And real-time reporting and analysis are simply out of the question.
In GA4, events are processed even if they arrive up to 72 hours late. Such events are called ‘late events’ as they are not sent immediately. That means it may take up to 3 full days for data to be fully processed and available in your reports.
You may see incomplete/inaccurate data and draw wrong conclusions if you analyse the data before it has been fully processed.
For example:
1) You may see a value of (not set) for a custom dimension during the first 24 hours after its creation.
2) Sometimes, you may need to wait for up to 48 hours for (not set) to disappear from your GA4 reports.
3) Server-side tracking can sometimes delay data processing, especially if your server is experiencing high traffic or latency. In such cases, data might not be available in GA4 reports immediately, and you could see (not set) values temporarily.
4) Data sent via the Measurement Protocol can be submitted with a delay, especially if it includes backfilling historical events.
5) If you use the GA4 data import feature to enrich your data, it can take time for the imported data to be processed and integrated with your standard event data.
6) Building and populating audiences, especially with more complex criteria, might not be instantaneous. It can take time for all users to be evaluated against the criteria of new or modified audiences.
7) If your GA4 property receives late events, it will take time for all events to align correctly with their respective sessions.
8) Some reports or metrics might update faster than others, leading to temporary inconsistencies between different views or summaries of your data.
9) GA4 aggregates data at different levels (e.g., user, session, event, item), and some of these aggregation processes can introduce delays, especially with large data volumes.
10) Sometimes, data might need corrections or adjustments due to filters, data imports, or other configurations. These adjustments can introduce additional processing time.
11) If you are integrating GA4 with Google Ads or other advertising platforms, there is often a delay in importing data, which can introduce temporary inconsistencies between different reports.

Other Articles on GA4.
- Tracking New, Qualified and Converted Leads in GA4.
- Free GA4 training and tutorial with Certification.
- Understanding GA4 Ecommerce Reports (Monetization Reports).
- GA4 Ecommerce Tracking via GTM: Step-by-Step Setup Guide.
- How to see UTM parameters in GA4 (Google Analytics 4).
- GA4 UTM parameters not working? Here is how to fix it.
- How To Use UTM parameters in GA4 (Campaign Tracking).
- How to track AI traffic in GA4.
- Understanding Google Analytics 4 cookies – _ga cookie.
- GA4 (Google Analytics 4) Measurement Protocol Tutorial.
- GA4 Unassigned Traffic: Causes and How to Fix it Fast.
- GA4 Regex (Regular Expressions) Tutorial.
- GA4 Direct Traffic Spike: Common Causes and How to Fix Them.
- gtag.js – Google Tag in Google Analytics 4 and beyond.
- GA4 Scopes – User, Session, Event & Item scopes.
- GA4 Conversion Tracking (Key Events) Tutorial.
- GA4 (not set) - Guide to fixing (not set) issue.
- GA4 Certification Exam: Questions, Answers for Skillshop (GAIQ).
- GA4 User Properties (User Scoped Custom Dimensions) – Tutorial.
- Tracking Organic Traffic in GA4 - Complete Guide.
- Tracking Events in GA4 (Google Analytics 4).
- GTM Server Side Tagging - Setup Guide.
- Using Subfolder for GTM Server Side Tagging (Same Origin Tracking).
- Understanding Event Parameters in Google Analytics 4 (GA4).
- How to Uninstall GTM Server Side Tagging.
- How to remove (other) in GA4 reports and avoid Cardinality.
- Creating GA4 Assistant via Claude for your customers.
- How To Set Up User ID in GA4 - Cross Device Tracking.
- GA4 Mobile App Tracking - Firebase Integration.

