In this article, I will show you how to write the same query (for extracting GA4 data in BigQuery) in 10 different ways and still produce the same/identical results.
You will learn what you have been missing out on, even as an experienced SQL user.
Consider the following base query:
SELECT
geo.continent,
geo.sub_continent,
geo.country,
geo.region,
geo.city,
COUNT(DISTINCT user_pseudo_id) AS total_users
FROM
`<Enter your table id here>`
WHERE
_TABLE_SUFFIX BETWEEN '20251001' AND '20251031'
AND user_pseudo_id IS NOT NULL
GROUP BY
geo.continent, geo.sub_continent, geo.country, geo.region, geo.city
ORDER BY
total_users DESC;Note: Use your table ID.
We will generate 10 different SQL versions of this query using different optimization strategies. All must produce identical results.
- Standard Baseline (direct)
- APPROX_COUNT_DISTINCT (speed)
- Pre-Deduplication (CTE + DISTINCT)
- Two-Stage Aggregation (distributed)
- STRUCT Grouping (compact)
- ARRAY_AGG Deduplication
- Window Function Approach
- Pre-Aggregated Session-Level (GA4-specific with ga_session_id)
- Materialized CTE (partition pruning)
- Nested Subquery (aggregation pushdown)

Version 1 - Standard Baseline (Clean and Direct).
SELECT
geo.continent,
geo.sub_continent,
geo.country,
geo.region,
geo.city,
COUNT(DISTINCT user_pseudo_id) AS total_users
FROM
`dbrt-ga4.analytics_207472454.events_*`
WHERE
_TABLE_SUFFIX BETWEEN '20251001' AND '20251031'
AND user_pseudo_id IS NOT NULL
GROUP BY
geo.continent, geo.sub_continent, geo.country, geo.region, geo.city
ORDER BY
total_users DESC;
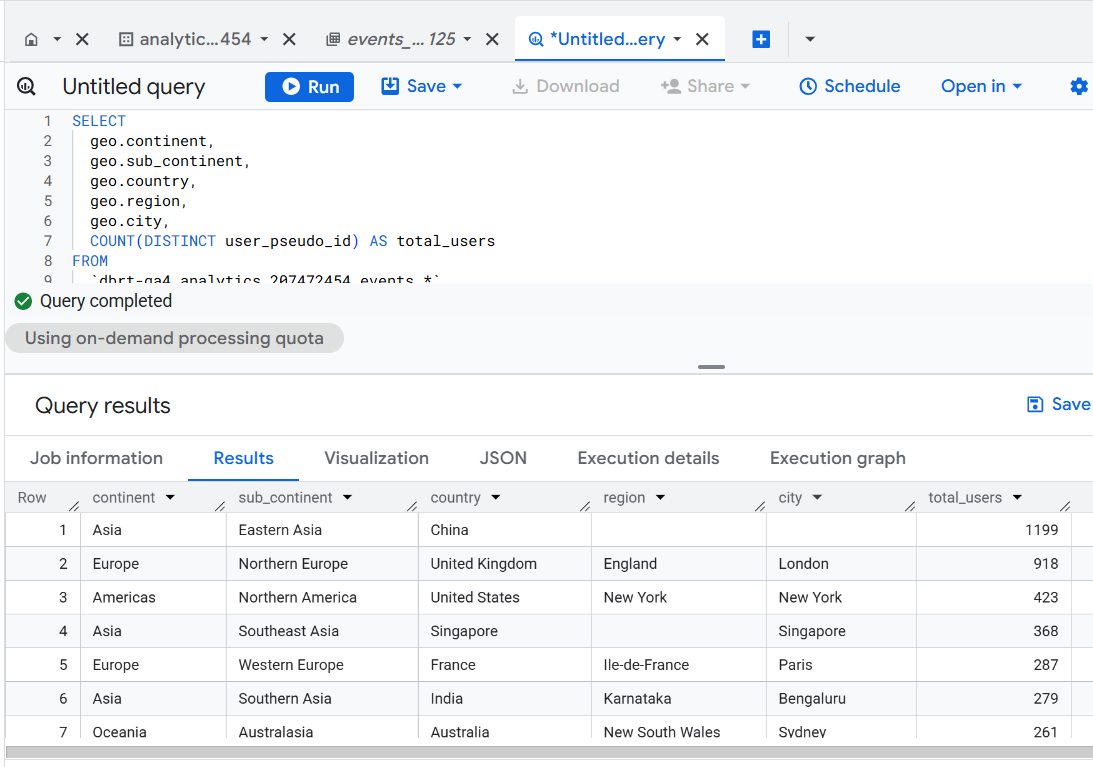
Use: Baseline reference for all versions.
Optimization Level: Medium (simple, readable, but full scan).
Version 2 - APPROX_COUNT_DISTINCT (Speed-Optimized).
SELECT
geo.continent,
geo.sub_continent,
geo.country,
geo.region,
geo.city,
APPROX_COUNT_DISTINCT(user_pseudo_id) AS total_users
FROM
`dbrt-ga4.analytics_207472454.events_*`
WHERE
_TABLE_SUFFIX BETWEEN '20251001' AND '20251031'
GROUP BY
geo.continent, geo.sub_continent, geo.country, geo.region, geo.city
ORDER BY
total_users DESC;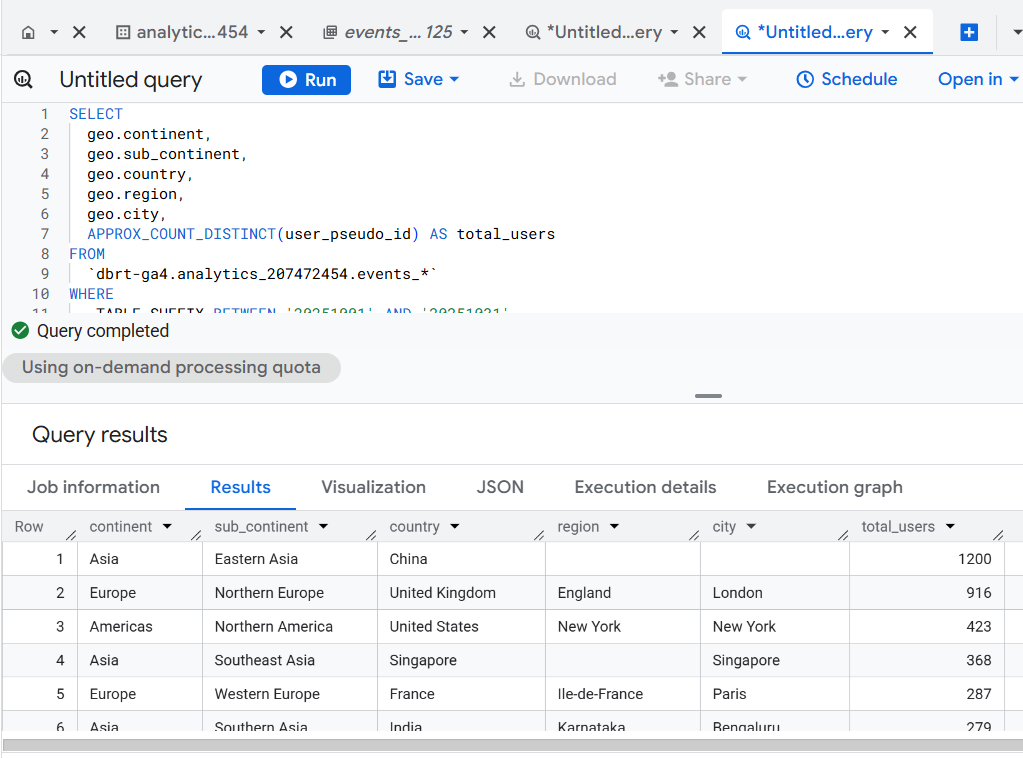
Use: Fast exploration/dashboards (minor accuracy loss <0.5%).
Optimization Level: High (fastest aggregation).
Version 3 - Pre-Deduplication (CTE with DISTINCT first).
WITH distinct_users AS (
SELECT DISTINCT
user_pseudo_id,
geo.continent AS continent,
geo.sub_continent AS sub_continent,
geo.country AS country,
geo.region AS region,
geo.city AS city
FROM
`dbrt-ga4.analytics_207472454.events_*`
WHERE
_TABLE_SUFFIX BETWEEN '20251001' AND '20251031'
AND user_pseudo_id IS NOT NULL
)
SELECT
continent,
sub_continent,
country,
region,
city,
COUNT(*) AS total_users
FROM
distinct_users
GROUP BY
continent, sub_continent, country, region, city
ORDER BY
total_users DESC; 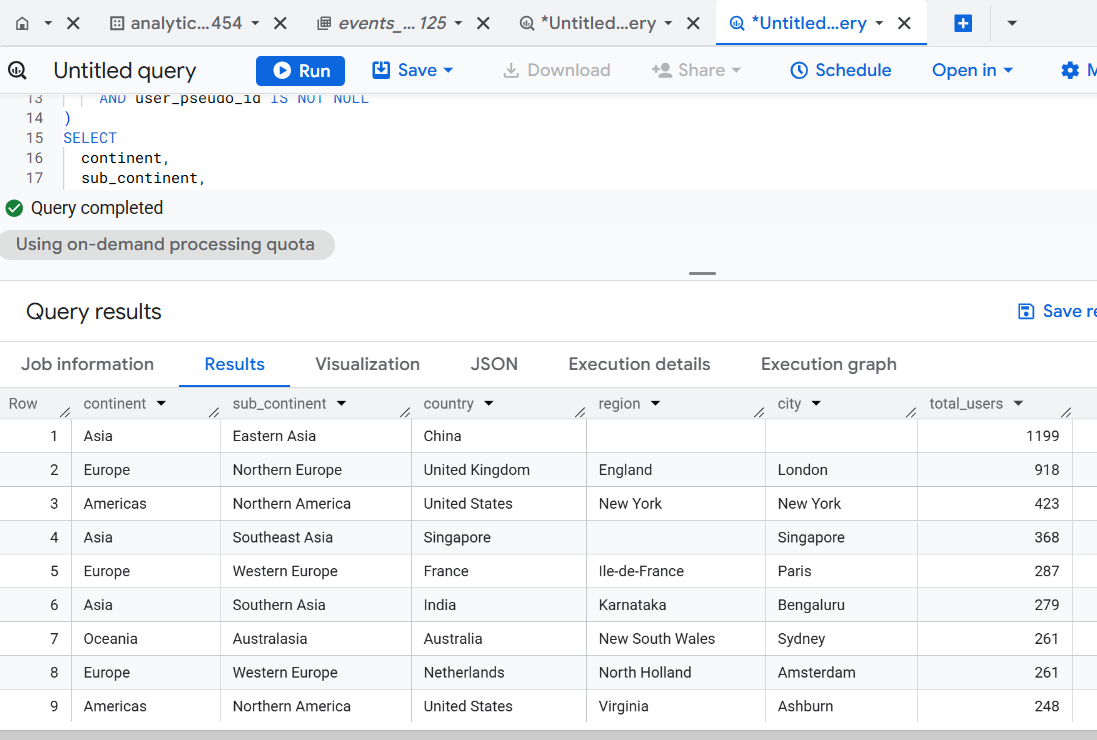
Use: When user-level deduplication reduces downstream scan costs.
Optimization Level: High for large, repetitive datasets.
Version 4 - Two-Stage Aggregation (Distributed).
-- Optimized: Two-stage aggregation for distributed processing
WITH stage1 AS (
-- Stage 1: Deduplicate each user-geo pair early
SELECT
user_pseudo_id,
geo.continent AS continent,
geo.sub_continent AS sub_continent,
geo.country AS country,
geo.region AS region,
geo.city AS city
FROM
`dbrt-ga4.analytics_207472454.events_*`
WHERE
_TABLE_SUFFIX BETWEEN '20251001' AND '20251031'
AND user_pseudo_id IS NOT NULL
GROUP BY
user_pseudo_id, continent, sub_continent, country, region, city
)
-- Stage 2: Aggregate distinct user counts per geography
SELECT
continent,
sub_continent,
country,
region,
city,
COUNT(*) AS total_users
FROM
stage1
GROUP BY
continent, sub_continent, country, region, city
ORDER BY
total_users DESC; 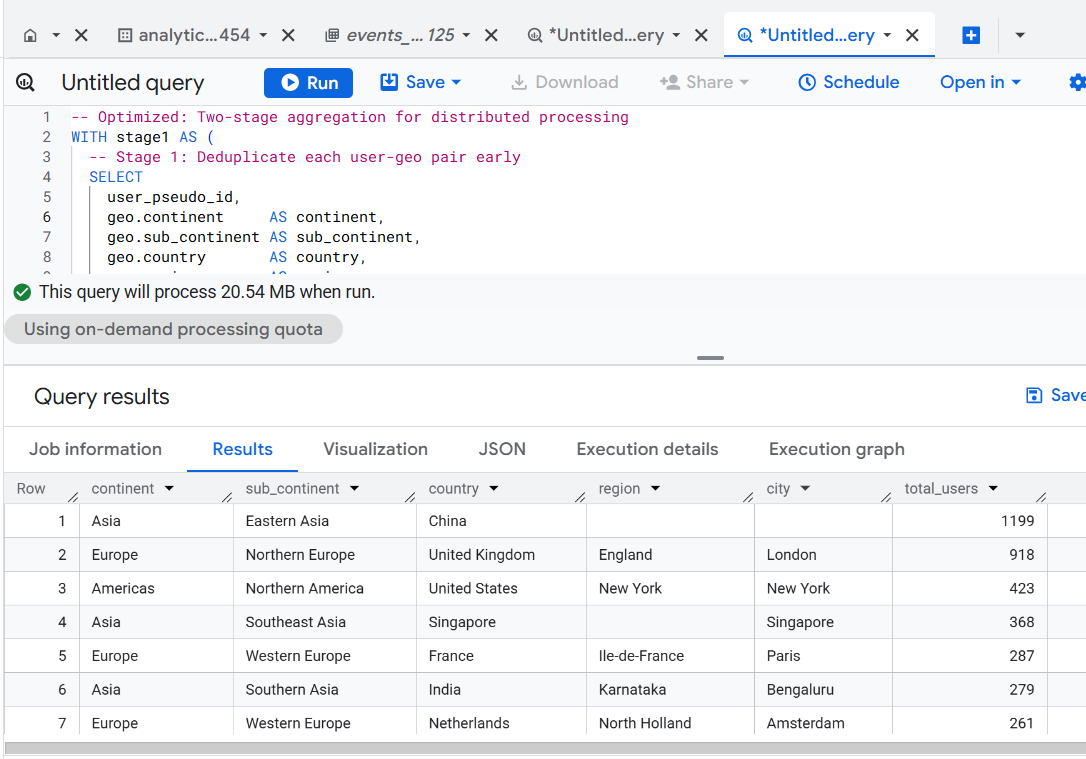
Use: Large-scale data where distributed intermediate results help cluster pruning.
Optimization Level: Very high (parallelism-friendly).

Version 5 - Using STRUCT Grouping (Compact Form).
SELECT
geo_group.continent,
geo_group.sub_continent,
geo_group.country,
geo_group.region,
geo_group.city,
COUNT(DISTINCT user_pseudo_id) AS total_users
FROM (
SELECT STRUCT(
geo.continent AS continent,
geo.sub_continent AS sub_continent,
geo.country AS country,
geo.region AS region,
geo.city AS city
) AS geo_group,
user_pseudo_id
FROM `dbrt-ga4.analytics_207472454.events_*`
WHERE _TABLE_SUFFIX BETWEEN '20251001' AND '20251031'
)
GROUP BY geo_group
ORDER BY total_users DESC; 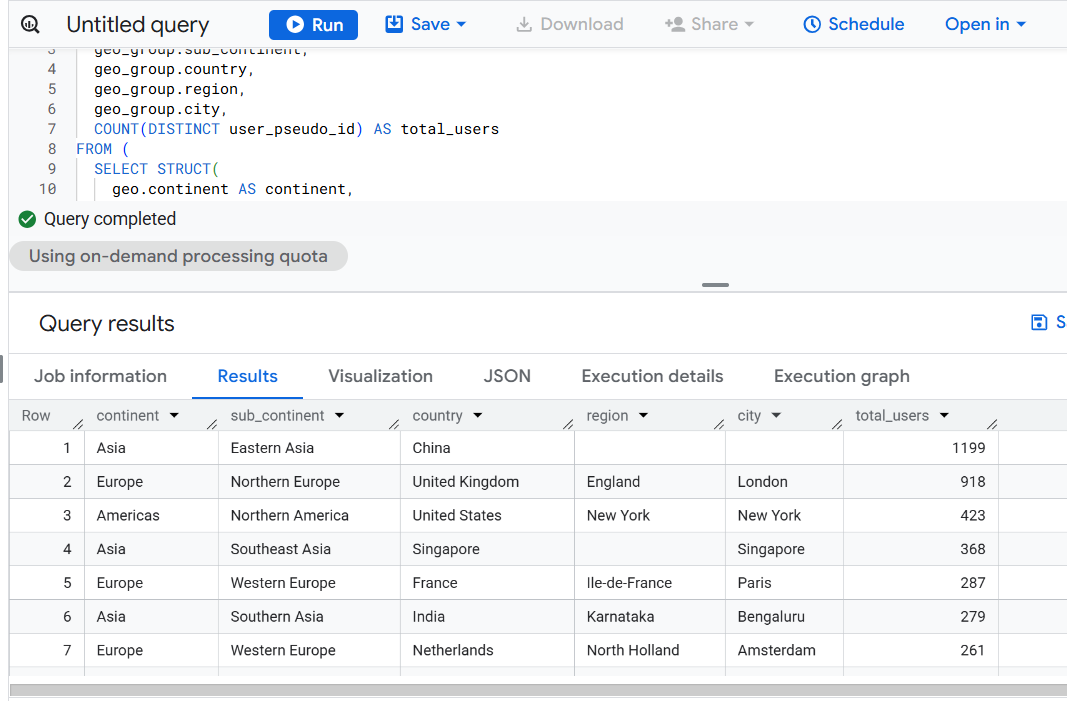
Use: For modular code or dynamic struct-based grouping (nested analytics).
Optimization Level: Medium-high (more compact grouping).
Version 6 - ARRAY_AGG Deduplication.
SELECT
geo.continent,
geo.sub_continent,
geo.country,
geo.region,
geo.city,
ARRAY_LENGTH(ARRAY_AGG(DISTINCT user_pseudo_id)) AS total_users
FROM
`dbrt-ga4.analytics_207472454.events_*`
WHERE
_TABLE_SUFFIX BETWEEN '20251001' AND '20251031'
GROUP BY
geo.continent, geo.sub_continent, geo.country, geo.region, geo.city
ORDER BY total_users DESC; 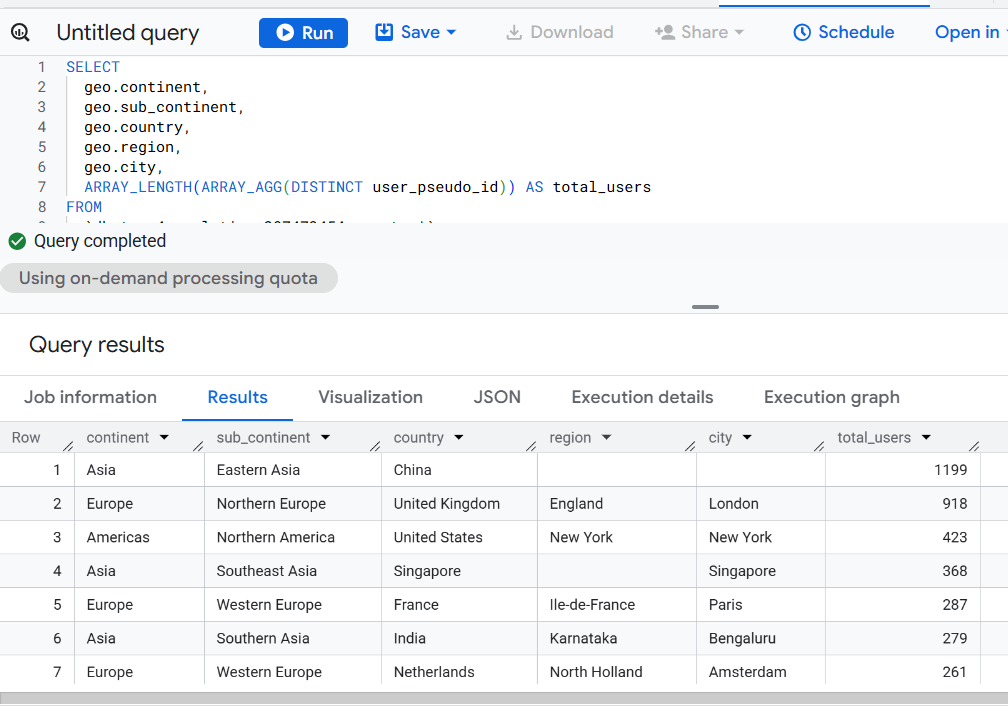
Use: When you also need user-level arrays for debugging or downstream joins.
Optimization Level: Moderate (higher memory footprint).
Version 7 - Window Function Approach (Analytic Reuse).
-- Optimized: Window function approach using explicit geo flattening
WITH distinct_user_geo AS (
SELECT DISTINCT
user_pseudo_id,
geo.continent AS continent,
geo.sub_continent AS sub_continent,
geo.country AS country,
geo.region AS region,
geo.city AS city
FROM
`dbrt-ga4.analytics_207472454.events_*`
WHERE
_TABLE_SUFFIX BETWEEN '20251001' AND '20251031'
AND user_pseudo_id IS NOT NULL
)
SELECT DISTINCT
continent,
sub_continent,
country,
region,
city,
COUNT(user_pseudo_id) OVER (
PARTITION BY continent, sub_continent, country, region, city
) AS total_users
FROM
distinct_user_geo
ORDER BY
total_users DESC; 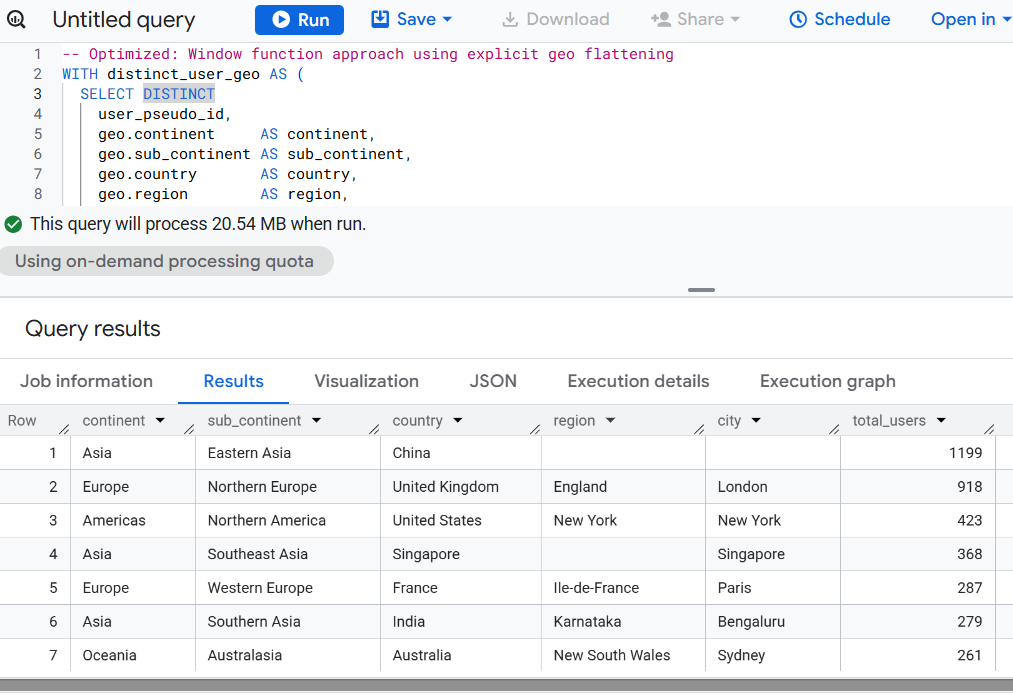
Use: When using analytic functions to mix multiple KPIs in one scan.
Optimization Level: Medium (not ideal for very large datasets).
Version 8 - Pre-Aggregated Session-Level Distinct Counting.
-- Approximate unique users by geo using pre-aggregated sessions.
WITH session_users AS (
SELECT
user_pseudo_id,
(SELECT value.int_value FROM UNNEST(event_params) WHERE key = 'ga_session_id') AS session_id,
geo.continent AS continent,
geo.sub_continent AS sub_continent,
geo.country AS country,
geo.region AS region,
geo.city AS city
FROM
`dbrt-ga4.analytics_207472454.events_*`
WHERE
_TABLE_SUFFIX BETWEEN '20251001' AND '20251031'
AND user_pseudo_id IS NOT NULL
),
unique_sessions AS (
-- Deduplicate user-session pairs (reduces row volume dramatically)
SELECT DISTINCT
user_pseudo_id,
session_id,
continent,
sub_continent,
country,
region,
city
FROM session_users
)
SELECT
continent,
sub_continent,
country,
region,
city,
COUNT(DISTINCT user_pseudo_id) AS total_users
FROM
unique_sessions
GROUP BY
continent, sub_continent, country, region, city
ORDER BY
total_users DESC; 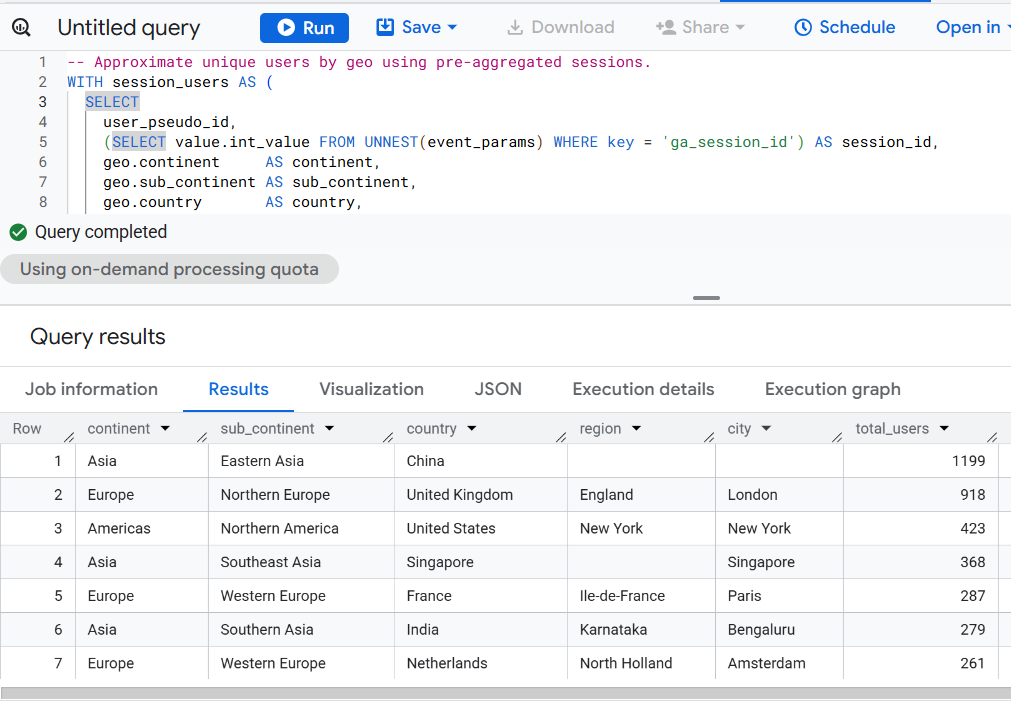
Use: For very large data with approximate distinct user counting.
Optimization Level: Very high (massively scalable).
Version 9 - Materialized CTE for Partition Pruning.
-- Materialized-style inline CTE for partition pruning
WITH filtered_events AS (
SELECT
user_pseudo_id,
geo.continent AS continent,
geo.sub_continent AS sub_continent,
geo.country AS country,
geo.region AS region,
geo.city AS city
FROM
`dbrt-ga4.analytics_207472454.events_*`
WHERE
_TABLE_SUFFIX BETWEEN '20251001' AND '20251031'
AND user_pseudo_id IS NOT NULL
)
SELECT
continent,
sub_continent,
country,
region,
city,
COUNT(DISTINCT user_pseudo_id) AS total_users
FROM
filtered_events
GROUP BY
continent, sub_continent, country, region, city
ORDER BY
total_users DESC; 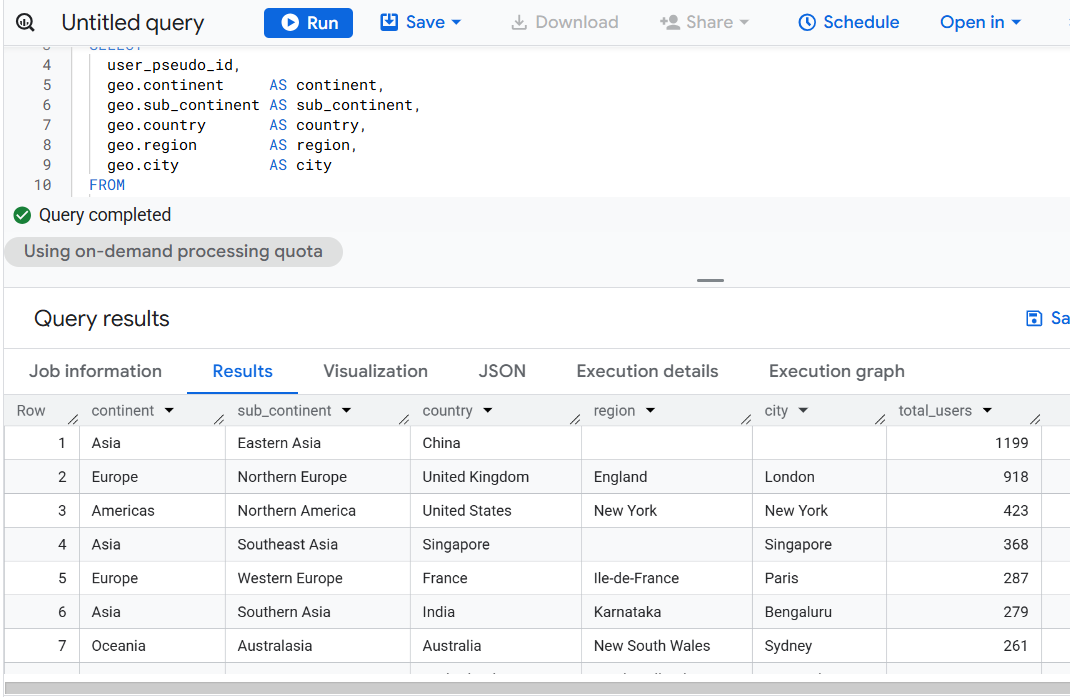
Use: When repeatedly querying the same partitioned subset.
Optimization Level: High (cached pre-filtering).
Version 10 - Nested Subquery for Aggregation Pushdown.
SELECT
continent,
sub_continent,
country,
region,
city,
SUM(user_count) AS total_users
FROM (
SELECT
geo.continent AS continent,
geo.sub_continent AS sub_continent,
geo.country AS country,
geo.region AS region,
geo.city AS city,
COUNT(DISTINCT user_pseudo_id) AS user_count
FROM `dbrt-ga4.analytics_207472454.events_*`
WHERE _TABLE_SUFFIX BETWEEN '20251001' AND '20251031'
GROUP BY continent, sub_continent, country, region, city
)
GROUP BY continent, sub_continent, country, region, city
ORDER BY total_users DESC; 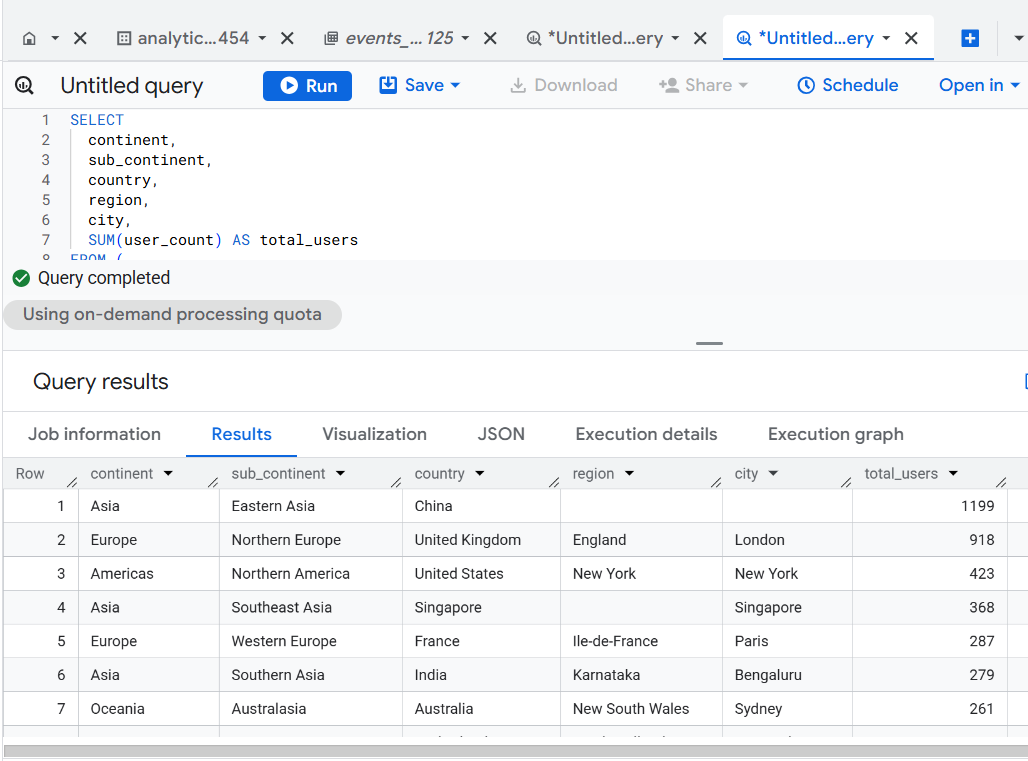
Use: For systems where pushing aggregates to nested levels improves caching.
Optimization Level: Medium-high.
Takeaways from the 10 SQL Versions Exercise.
1. There Is No Single Correct SQL.
Ten completely different SQL queries produced identical results.
This proves that SQL is not about finding "the right answer", it's about choosing the right approach for your specific context.
2. Same Output, Different Performance.
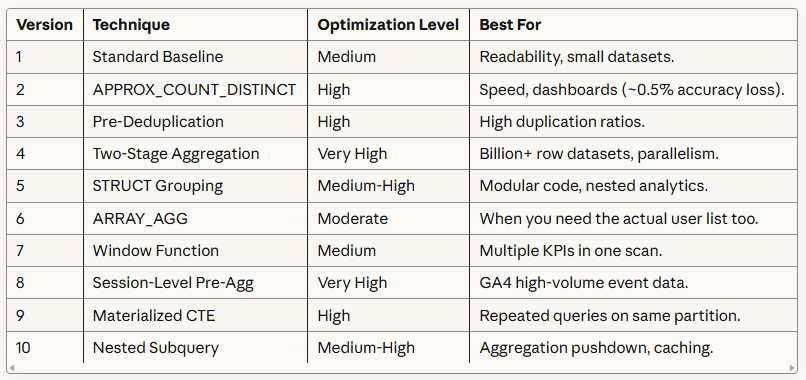
Same result. Vastly different speed, cost, and scalability.
3. Context Determines the Best Choice.
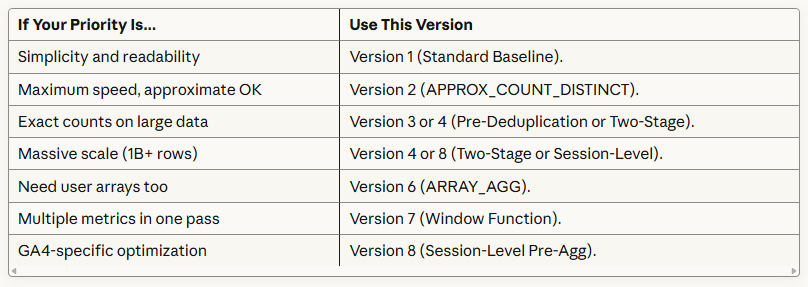
4. Manual SQL Generation Will Drive You Mad.
Writing 10 optimized versions manually would take days. Yet an AI can generate all 10 in seconds. This raises the question:
Why spend time hand-crafting SQL when you can:
- Define your requirements first.
- Let AI recommend the best technique.
- Generate optimized SQL automatically.
===============================
If you want to learn how to generate optimized GA4 BigQuery SQL like this without writing a single line of code yourself, check out my GA4 BigQuery Course, where I teach you the underlying logic for GA4 dimensions and metrics, so you can use Vibe Coding to generate any SQL query in seconds.
No SQL experience required.
Just describe what you want. Let AI do the rest.
Related Articles:
- GA4 to BigQuery Mapping Tutorial.
- Understanding the BigQuery User Interface.
- GA4 BigQuery Query Optimization.
- How to access a nested field in GA4 BigQuery data table.
- How to Calculate Unique Users in GA4 BigQuery.
- GA4 BigQuery Export Schema Tutorial.
- Calculating First Time Users in GA4 BigQuery.
- Extracting Geolocations in GA4 BigQuery.
- GA4 BigQuery SQL Optimization Consultant.
- Tracking Pages With No Traffic in GA4 BigQuery.
- First User Primary Channel Group in GA4 BigQuery
- How to handle empty fields in GA4 BigQuery.
- Extracting GA4 User Properties in BigQuery.
- Calculating New vs Returning GA4 Users in BigQuery.
- How to access BigQuery Public Data Sets.
- How to access GA4 Sample Data in BigQuery.

