In BigQuery, you can use a dozen different optimisation techniques to produce the same result.
There's no single "best" way to query data because queries serve vastly different purposes:
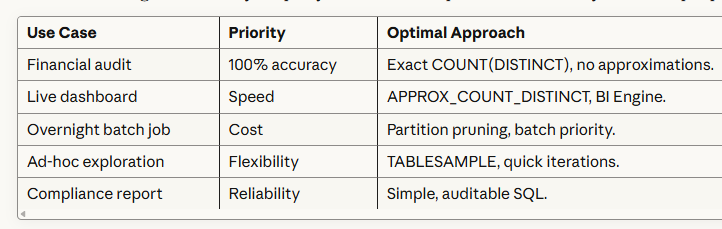
One technique cannot serve all these needs optimally.
Every optimization involves trade-offs:
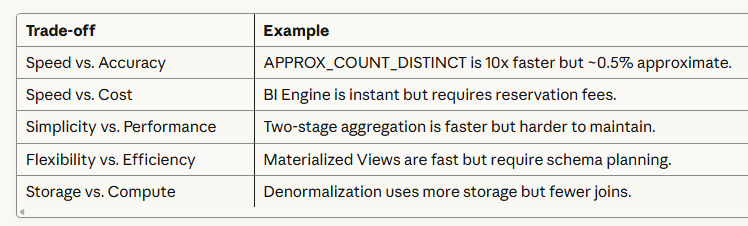
BigQuery provides multiple techniques so you can choose the right trade-off for your situation.
3. BigQuery's Architecture Creates Options.
BigQuery's distributed, columnar architecture enables many optimization paths:
Storage Layer Optimizations:
- Partitioning (reduce data scanned).
- Clustering (reduce blocks read).
- Columnar storage (select only needed columns).
Compute Layer Optimizations:
- Approximate functions (reduce memory/CPU).
- Broadcast vs. hash joins (reduce shuffling).
- BI Engine (in-memory acceleration).
Caching Layer Optimizations:
- Query result cache (24-hour automatic).
- Materialized views (pre-computed results).
- Destination tables (manual caching).
Each layer offers different optimization levers.

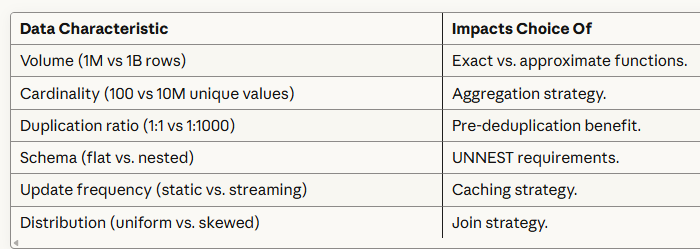
4. Data Characteristics Vary Widely.
The "best" technique depends heavily on your data:
The $10,000 Query Problem.
Picture this: You're a data analyst tasked with counting unique users by geographic location from your GA4 data. You write what seems like a straightforward query:
-- Calculate the total number of unique users by geo locations.
SELECT
geo.continent AS continent,
geo.sub_continent AS sub_continent,
geo.country AS country,
geo.region AS region,
geo.city AS city,
COUNT(DISTINCT user_pseudo_id) AS total_users
FROM
`project.analytics_123456789.events_*`
WHERE
_TABLE_SUFFIX BETWEEN '20251001' AND '20251031'
GROUP BY
continent,
sub_continent,
country,
region,
city
ORDER BY
total_users DESC;You hit run. 45 seconds later, you get your results. The query scanned 500GB of data and cost $2.50.
Not bad for a one-time query, right?
But this query runs daily. That's $912.50 per year for a single report. And you have dozens of similar queries.
Suddenly, your BigQuery bill is climbing toward five figures, for queries that could run in 3 seconds and cost 80% less.
The problem isn't BigQuery.
It's that you chose the wrong optimization technique before you started writing.

Why Most SQL Optimization Fails?
Traditional SQL optimization follows a broken workflow:
Write Query → Run Query → Notice it's slow → Try to optimize → Rewrite → Repeat.This approach has three fatal flaws:
1. It's reactive, not proactive - You don't discover performance problems until after you've invested time writing complex SQL. By then, you're emotionally attached to your solution and reluctant to start over.
2. It ignores context - A query that's perfect for a one-time analysis is terrible for a real-time dashboard. The "best" SQL depends entirely on your specific requirements, accuracy needs, data volume, query frequency, and performance goals.
3. It assumes one-size-fits-all - There are at least 10 different optimization techniques for counting unique values in BigQuery alone. Most analysts know one or two. They use a hammer for every problem, even when they need a scalpel.
Introducing the GA4 BigQuery SQL Optimization Consultant.
The GA4 BigQuery SQL Optimization Consultant is a mega text prompt used inside GA4 BigQuery Composer that flips the traditional workflow on its head. It is rolling out to all the students of the GA4 BigQuery Course.
Define Requirements → Choose Best Technique → Write Optimized SQL.Instead of writing SQL and hoping for the best, the Consultant asks you targeted questions about your specific use case, then recommends the optimal optimization strategy before any code is written.
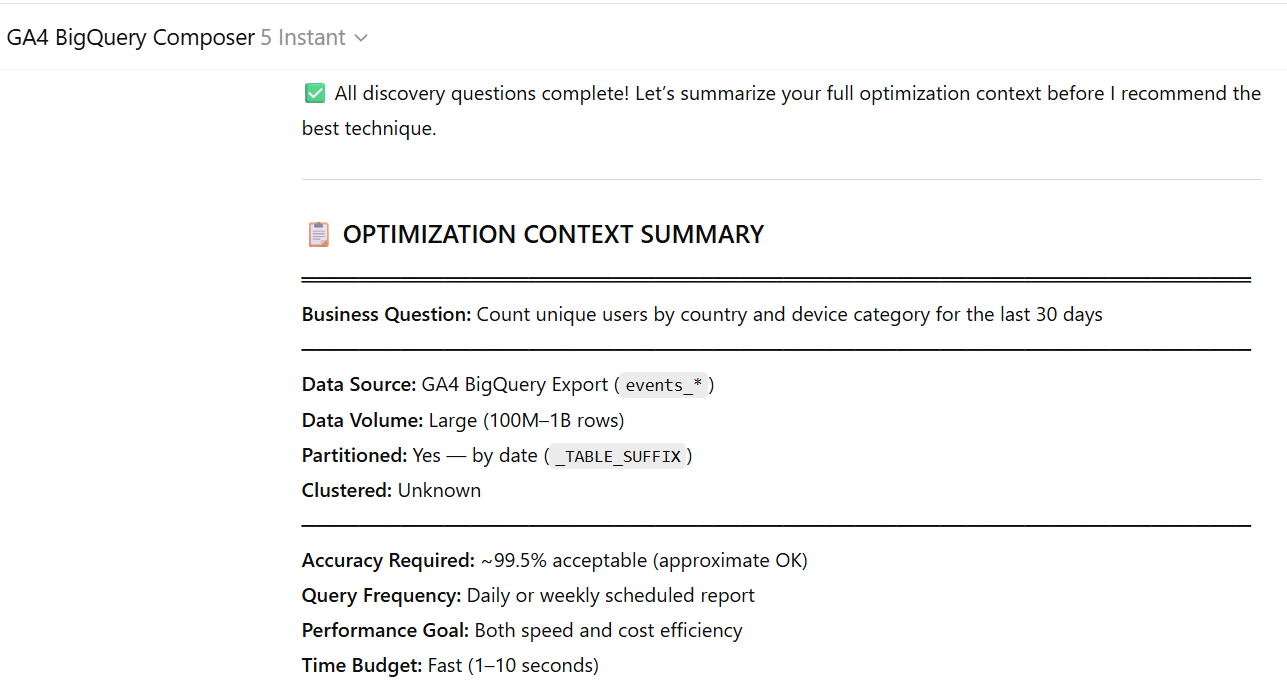
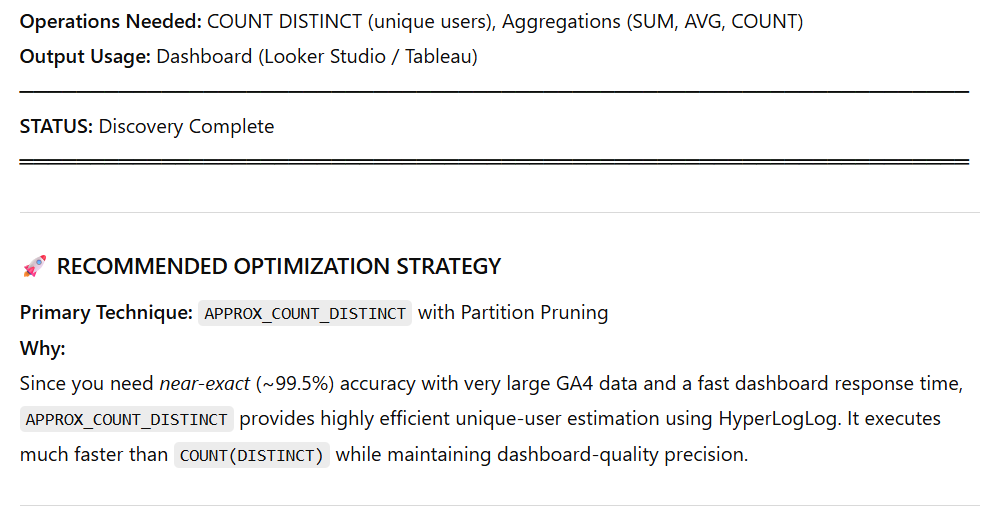
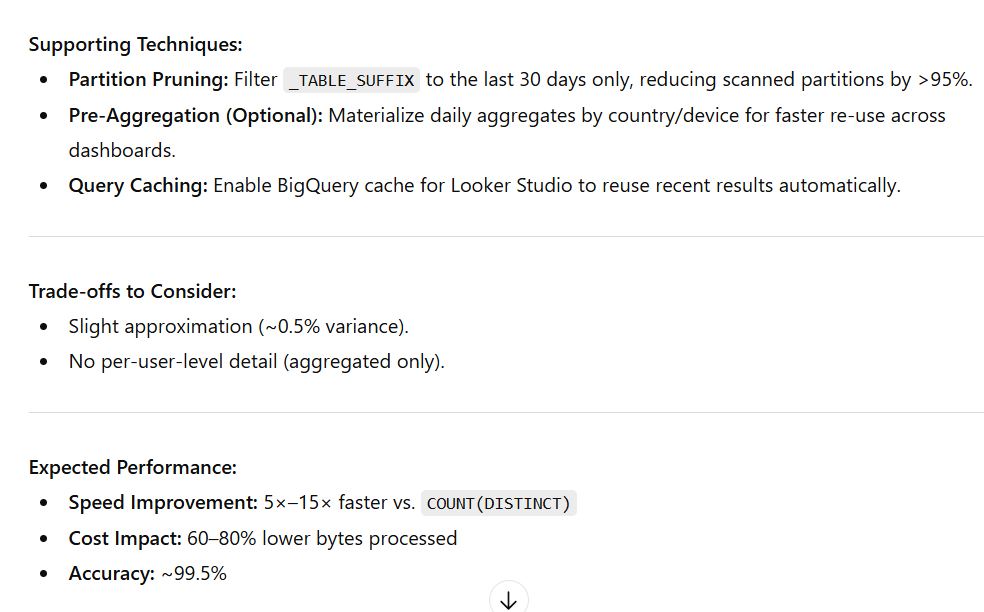

Does the Consultant Cover All Techniques?
Honest Answer: No, and that's by design.
The BigQuery SQL Optimization Consultant focuses on the most impactful techniques for common analytical queries, not every possible optimization.
What does the Consultant Cover Well?
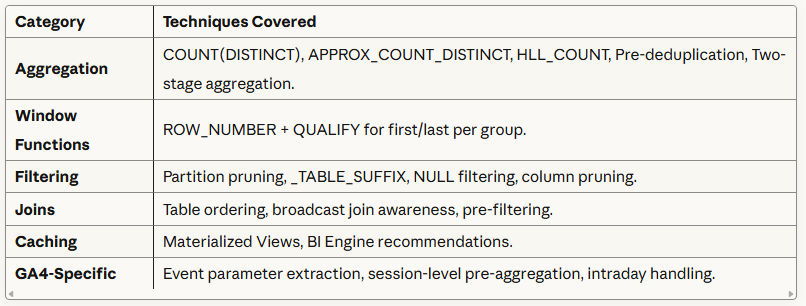
Coverage: ~70-80% of common analytical query optimization needs.
What does the Consultant Cover Partially?
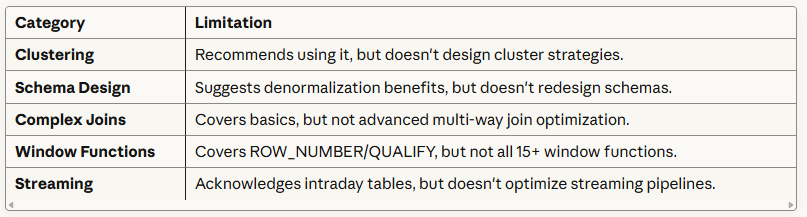
What the Consultant Does NOT Cover?
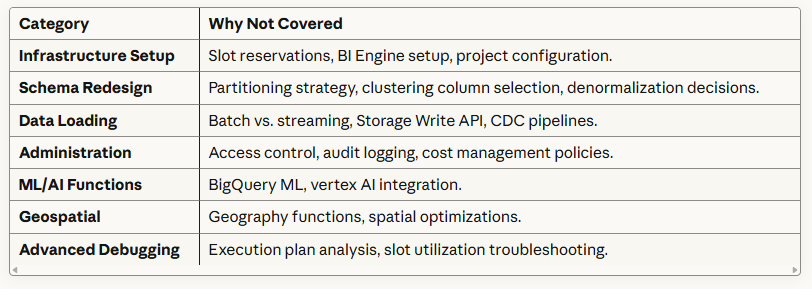
Why the Consultant Focuses on a Subset?
The 80/20 Rule: 80% of query performance problems come from 20% of optimization decisions:
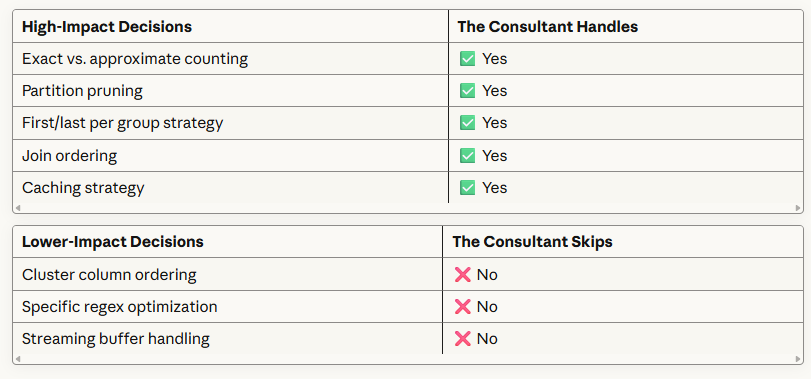
The magic isn't knowing these techniques exist, it's knowing which one to use when.
The Bottom Line.
Writing SQL without first determining the right optimization technique is like building a house without blueprints.
You might end up with something functional, but you'll waste time, money, and materials getting there.
The BigQuery SQL Optimization Consultant ensures you choose the right approach from the start, saving you countless hours of trial and error, thousands of dollars in query costs, and the frustration of slow, expensive reports.

Related Articles:
- GA4 to BigQuery Mapping Tutorial.
- Understanding the BigQuery User Interface.
- GA4 BigQuery Query Optimization.
- How to access a nested field in GA4 BigQuery data table.
- How to Calculate Unique Users in GA4 BigQuery.
- GA4 BigQuery Export Schema Tutorial.
- Calculating First Time Users in GA4 BigQuery.
- Extracting Geolocations in GA4 BigQuery.
- GA4 BigQuery SQL Optimization Consultant.
- Tracking Pages With No Traffic in GA4 BigQuery.
- First User Primary Channel Group in GA4 BigQuery
- How to handle empty fields in GA4 BigQuery.
- Extracting GA4 User Properties in BigQuery.
- Calculating New vs Returning GA4 Users in BigQuery.
- How to access BigQuery Public Data Sets.
- How to access GA4 Sample Data in BigQuery.
- Understanding engagement_time_msec in GA4 BigQuery.

