GA4 does not report on pages that received no traffic (zero pageviews) during the selected time period.
However, it does report on the pages that had zero pageviews on some days and one or more on others within that same period.
This means “no traffic” is dependent on the timeframe you choose.
Pages with zero pageviews do not contribute to your business goals because they generate no traffic.
By identifying these pages, you can either improve them to boost their search performance or repurpose their content.
If a web page had fewer than 30 pageviews in the last month, it means it had zero pageviews on at least one day.
This is the easiest method to determine zero-traffic pages on your website.
We would need the ‘landing page’ dimension and the ‘views’ metric to create the report that tracks web pages with zero pageviews in GA4 BigQuery.

#1 In BigQuery, you can calculate the values of the ‘Landing Pages’ dimension by extracting the values from the ‘page_location’ event parameter where 'event_name' top level field is 'page_view' and the value of 'entrances' event parameter is 1.
#2 Calculate the values of the ‘Views’ metric by counting the total number of 'page_view' events for each 'Landing Page'.
#3 We only want those rows of the data table where the value of 'Views' for each landing page is less than 30.
Once you understand the logic, tracking web pages with zero pageviews via text prompt is easy.
The SQL below is automatically generated via a text prompt in GA4 BigQuery Composer (a custom chatGPT) that calculates unique users in GA4 BigQuery:
-- Tracking web pages with zero pageviews in GA4
WITH
prep AS (
SELECT
(
SELECT value.string_value
FROM UNNEST(event_params)
WHERE key = 'page_location'
) AS page_location,
(SELECT value.int_value FROM UNNEST(event_params) WHERE key = 'entrances')
AS entrances_int,
event_name
FROM
`dbrt-ga4.analytics_207472454.events_*`
WHERE
_TABLE_SUFFIX BETWEEN '20251001' AND '20251031'
)
SELECT
CASE
WHEN
page_location IS NULL
OR page_location = ''
OR page_location = 'https://optimizesmart.com/'
THEN '(not set)'
ELSE page_location
END AS landing_pages,
COUNT(*) AS views
FROM
prep
WHERE
event_name = 'page_view'
AND entrances_int = 1
GROUP BY
landing_pages
HAVING
COUNT(*) < 30
ORDER BY
views ASC;
Note: Use your table ID. Otherwise, the code would not work.
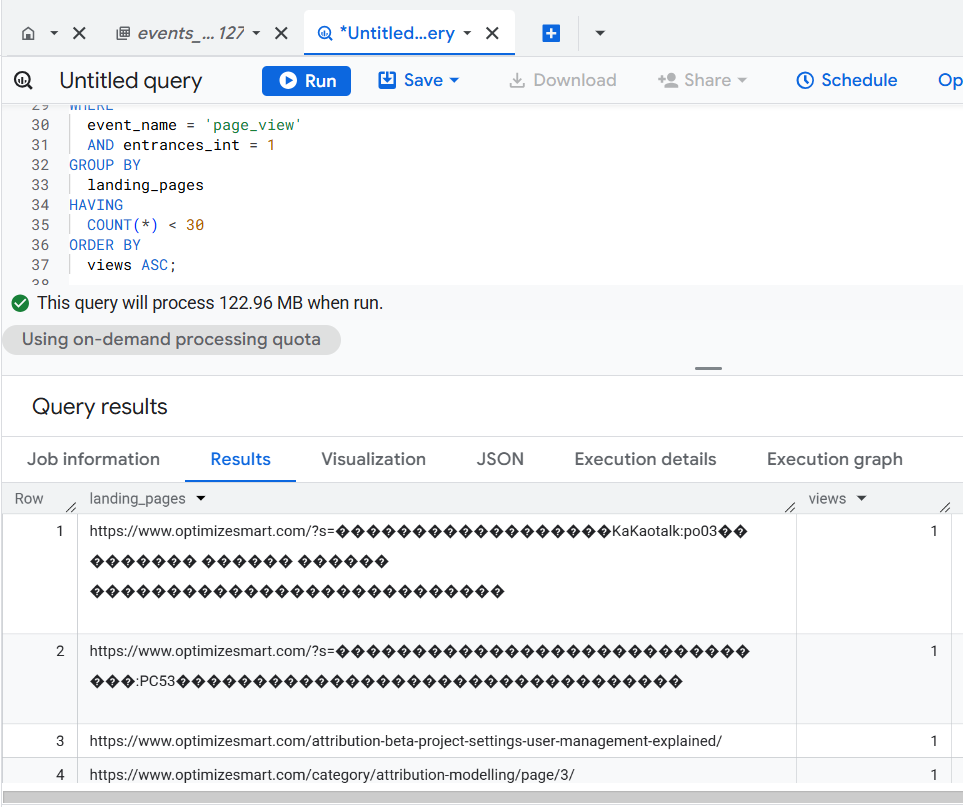
Now I want to filter out all the pages where people performed a search. That way, I get a cleaner report.
I can add the following sentence to my existing prompt:
Filter out all those rows of the data table where the value of ‘page_location’ event parameter starts with https://www.optimizesmart.com/?s=
Then I get the following AI generated SQL:
-- Tracking web pages with zero pageviews in GA4
WITH
prep AS (
SELECT
(
SELECT value.string_value
FROM UNNEST(event_params)
WHERE key = 'page_location'
) AS page_location,
(SELECT value.int_value FROM UNNEST(event_params) WHERE key = 'entrances')
AS entrances_int,
event_name
FROM
`dbrt-ga4.analytics_207472454.events_*`
WHERE
_TABLE_SUFFIX BETWEEN '20251001' AND '20251031'
)
SELECT
CASE
WHEN
page_location IS NULL
OR page_location = ''
OR page_location = 'https://optimizesmart.com/'
THEN '(not set)'
ELSE page_location
END AS landing_pages,
COUNT(*) AS views
FROM
prep
WHERE
event_name = 'page_view'
AND entrances_int = 1
AND (
page_location IS NULL
OR NOT STARTS_WITH(page_location, 'https://www.optimizesmart.com/?s='))
GROUP BY
landing_pages
HAVING
COUNT(*) < 30
ORDER BY
views ASC;
Now my report looks much cleaner:
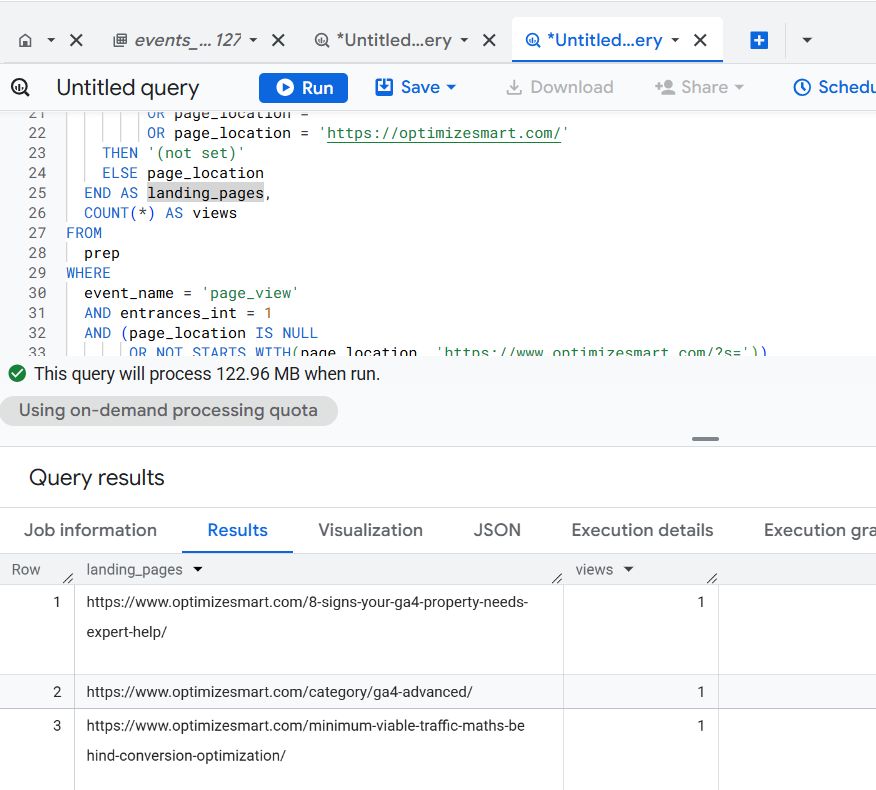
As you can see, the first SQL is 37 lines of code and the second SQL is 39 lines of code.
But since I used AI, it took me less than 5 minutes to go from design to production ready SQL.
The ‘design’ part is where I understand the logic and craft my text prompt. This is the most time consuming part.
Generating the required SQL takes only a couple of seconds.
If you hand-craft these two SQL logics, it could be a couple of hours' work depending on your skill set.
Regardless, that’s how you can track web pages with zero traffic in GA4 BigQuery.
======================
Learn the underlying logic for calculating various GA4 dimensions and metrics in BigQuery and leave the actual SQL generation to ChatGPT.
Your GA4 BigQuery data is only as good as the query logic you use. Once you understand the query logic, you can scale across 'N' SQL use cases.
That's what I teach in my GA4 BigQuery Course. The focus is entirely on teaching the underlying logic (instead of the actual SQL).

Related Articles:
- GA4 to BigQuery Mapping Tutorial.
- Understanding the BigQuery User Interface.
- GA4 BigQuery Query Optimization.
- How to access a nested field in GA4 BigQuery data table.
- How to Calculate Unique Users in GA4 BigQuery.
- GA4 BigQuery Export Schema Tutorial.
- Calculating First Time Users in GA4 BigQuery.
- Extracting Geolocations in GA4 BigQuery.
- GA4 BigQuery SQL Optimization Consultant.
- Tracking Pages With No Traffic in GA4 BigQuery.
- First User Primary Channel Group in GA4 BigQuery
- How to handle empty fields in GA4 BigQuery.
- Extracting GA4 User Properties in BigQuery.
- Calculating New vs Returning GA4 Users in BigQuery.
- How to access BigQuery Public Data Sets.
- How to access GA4 Sample Data in BigQuery.

